Power Supply User Manual
S1F76640 Series
S1F70000 Series EPSON 2–57
Technical Manual
S1F76640
Series
APPLICATION EXAMPLE
2 Times Step-up, 3 Times Step-up and 4 Times Step-up
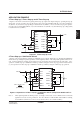
Figure 8.1 shows the connection for getting 4 times step-up output of an input voltage by operating the step-up
circuit only. In case of 3 times step-up, the capacitor C
3 is removed and CAP3+ (Pin No. 14) is short-circuited to
V
O (Pin No. 15), and 3 times step-up voltage is obtained from VO(CAP3+). In case of 2 times step-up, the capacitor
C
2 is also removed and CAP2+ (Pin No. 13) is short-circuited to VO (Pin No. 15), and 2 times step-up voltage (10V)
is obtained from V
O (CAP2+).
Figure 8-1 4 times step-up circuit
4 Times Step-up + Stabilization Circuit
Figure 8-2 shows an application example for stabilizing step-up outputs obtained in 8-(1) through the stabilization
circuit and for providing temperature gradient to V
REG output by means of the temperature gradient selection cir-
cuit. In this application example, both outputs from V
O and VREG can be indicated at the same time. Also,
operation of 3 times step-up + stabilization circuit is possible by using the 3 times step-up operation mentioned in 8-
(1), and operation of 2 times step-up + stabilization circuit is possible by using the 2 times step-up operation.
Figure 8-2 Operation of 4 Times Step-up + Stabilization Circuit (Temperature Gradient CT1 is
selected.)
Note 1 : Since input impedance at the RV pin (No. 1) is high, it is necessary to use a shielded wire as a measure
against noise in case of a long connection. It is also effective to make the R
RV value small for reducing
noise influence. (In this case, however, more current comes to be consumed at R
RV.)
C
1
V
I
C
2
C
3
C
4
4V
I
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
RV
V
REG
TC1
TC2
P
OFF
V
SS
OSC1
OSC2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
RI
V
O
CAP3+
CAP2+
CAP2–
CAP1+
CAP1–
V
DD
RV
V
REG
TC1
TC2
P
OFF
VSS
OSC1
OSC2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
RI
VO
CAP3+
CAP2+
CAP2–
CAP1+
CAP1–
V
DD
C2
C5
+
–
C
1
+
–
C
3
+
–
C
4
VI
R1
R1
R1+R2
R2
+
–
+
–
Note 1
V
REG= ·VRV
VREG
(RRV=R1+R2)
Note 2