Instruction manual
Table Of Contents
- 1. INTRODUCTION
- 2. GETTING STARTED
- 3. CONDUCTIVITY ELECTRODE
- 4. PH AND MV CALIBRATION
- 5. CONDUCTIVITY AND TDS CALIBRATION
- 6. CONDUCTIVITY AND TDS MEASUREMENT
- 7. HOLD FUNCTION
- 8. STORING AND RECALLING DATA
- 9. SETUP FUNCTIONS
- 9.1 1.0 CAL (Calibration)
- 9.2 2.0 ELE (Electrode Information)
- 9.3 3.0 ConF (Configuration)
- 9.4 3.1 rdY (Ready / Stability Indicator)
- 9.5 3.2 ºC ºF (Celsius or Fahrenheit)
- 9.6 3.3 buFF (pH Buffers & Calibration Points)—pH only
- 9.7 3.3 AtC (Auto Temp Compensation)—Con & TDS only
- 9.8 3.4 tdS (TDS factor)—Con & TDS only
- 9.9 3.5 t.CO (Temperature Coefficient)—Con & TDS only
- 9.10 3.6 t.nr (Normalization Temperature in ºC)—Con & TDS only
- 9.11 3.7 ACAL (Auto Conductivity Calibration)—Con & TDS only
- 9.12 3.8 SPC (Single Point Calibration)—Con & TDS only
- 9.13 3.8 CELL (Nominal Cell Constant)—Con & TDS only
- 9.14 4.0 rSt (Reset)
- 9.15 5.0 CLr (Clear Memory)
- 10. CALCULATING TDS CONVERSION FACTOR
- 11. CALCULATING TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENTS
- 12. REPLACEMENTS AND ACCESSORIES
- 13. TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
- 14. SPECIFICATIONS
- 15. WARRANTY
- 16. RETURN OF ITEMS
- info@4oakton.comwww.4oakton.com
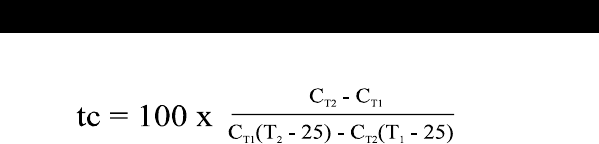
11. CALCULATING TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENTS
To determine the temperature coefficient of your sample solution use this
formula:
Where:
tc = Temperature coefficient 25 = 25 ºC
C
T1
= Conductivity at Temp 1 C
T2
= Conductivity at Temp 2
T1 = Temp 1 T2 = Temp 2
NOTE: A controlled temperature water bath is ideal for this procedure.
1. Immerse the probe into a sample of your solution and adjust the
temperature coefficient to 0% (that is, no compensation) by following
instructions as described in Section 9.9.
2. Wait for 5 minutes. Note T1 and CT1 (conductivity at T1).
3. Condition the sample solution and probe to a temperature (T2) that is
about 5 ºC to 10 ºC different from T1, and note the conductivity
reading C
T2
.
NOTE: Record your results for future reference. Ideally T1 and T2 should
bracket your measurement temperature, and should not differ by
more than 5 ºC.
4. Calculate the temperature coefficient of your solution according to the
formula shown above.
5. Enter the calculated temperature coefficient into the meter.
The calculated temperature coefficient will now be applied to all the meter
readings.
18










