User Manual
Table Of Contents
- E7 IC Card Reader Introduction
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 Features
- 1.3 Device Interface
- 1.4 Peader Packing List
- 1.5 Software
- 1.6 Reader Type Description
- 1.7 Function Instruction
- 1.8 API Function List
- Common Functions
- Device Function
- Keyboard Specific Functions
- S50 card functions
- S70 card specific function
- Ultralight card specific function
- Ultralight-C card specific function
- Mifare pro card specific function
- Mifare PLUS card specific function
- Contactless CPU card(ISO14443) specific function
- Desfire card specific function
- CPU(SAM) card specific functions
- 4442 card-specific functions
- 4428 Card-Specific Functions
- 1.9 Error codes and Meanings
- 2. API Function
- 2.1 Common Functions
- 2.2 Device Functions
- 2.3 Keyboard Special Functions
- 2.4 S50(M1)Functions
- 2.5 S70 card specific function
- 2.6 Ultralight card specific function
- 2.7 Ultralight-Ccard specific function
- 2.8 Mifare Pro card specific function
- 2.9 Contactless CPU card(ISO1443) specific functi
- 2.10 Desfirecard specific function
- 2.11 Mifare Plus card specific function
- 2.12 CPU(SAM)Functions
- 2.13 SLE4442 special Functions
- 2.14 SLE4428 special Functions
- 3.MIFARE ONE Card Structure
- 4.Appendix
67
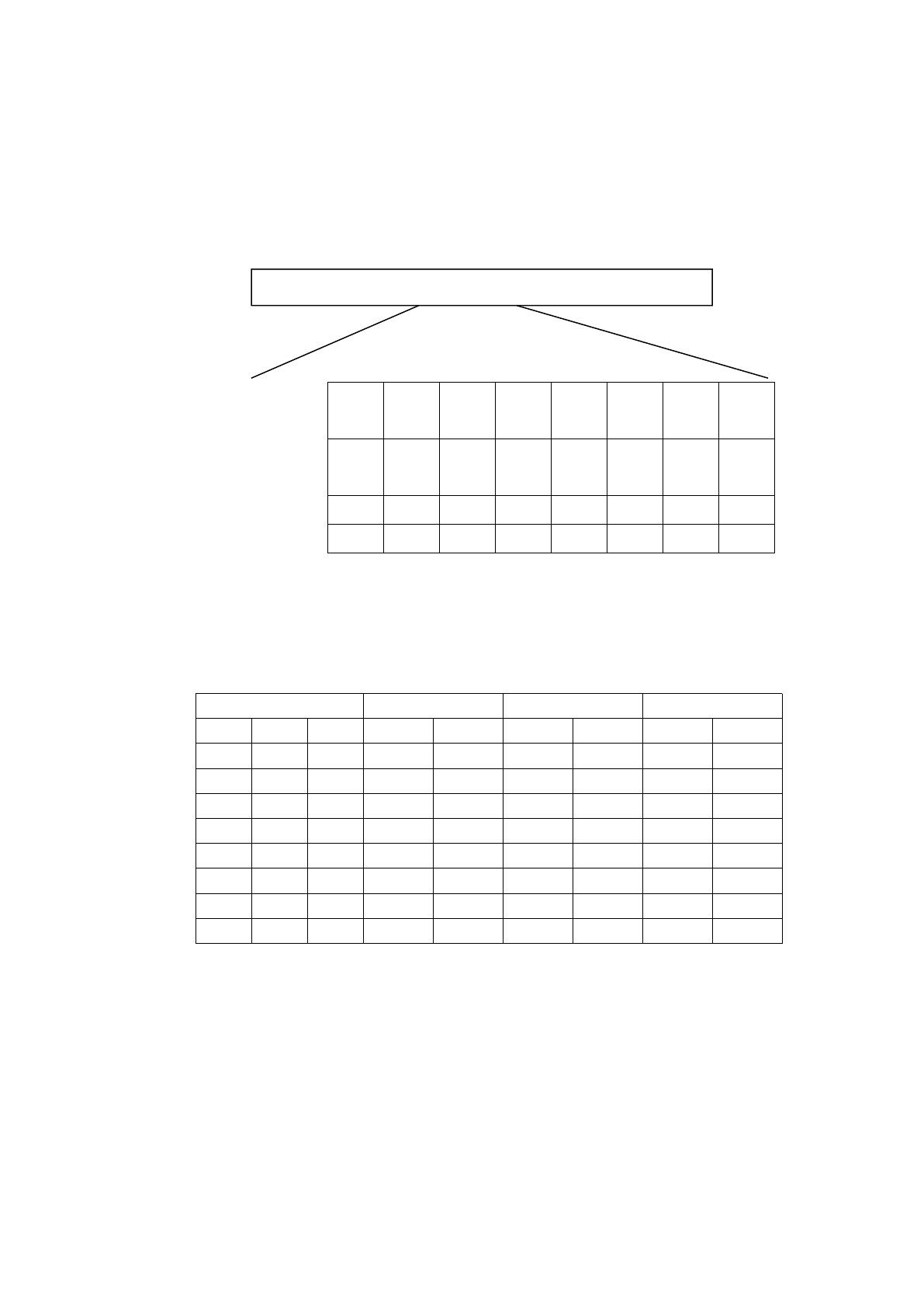
Three control bits exists in the access control byte by positive or negative form,
determines access rights to the block (such as impairment operation must verify KEY
A, for value-added operations must verify KEY B, etc). the position of three control
bits in the access control byte as follows (byte 9 is spare byte, default is 0x69):
keyA control bits key B
bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Byte 6
C23_
b
C22_
b
C21_
b
C20_
b
C13_
b
C12_
b
C11_
b
C10_
b
Byte 7
C13
C12
C11
C10
C33_
b
C32_
b
C31_
b
C30_
b
Byte 8
C33
C32
C31
C30
C23
C22
C21
C20
Byte 9
(remark:_b means negation ,For example: if c11 is 1, c11_b is 0; c11 is
0, c11_b is 1 )
1. Control block(block 3)the acess control of block 3 is different from the data
block(blocks 0,1,2), its access control are as follows:
key A
Control bit
Key B
C13
C23
C33
Read
Write
Read
Write
Read
Write
0
0
0
Never
KeyA|B
KeyA|B
Never
KeyA|B
KeyA|B
0
1
0
Never
Never
KeyA|B
Never
KeyA|B
Never
1
0
0
Never
KeyB
KeyA|B
Never
Never
KeyB
1
1
0
Never
Never
KeyA|B
Never
Never
Never
0
0
1
Never
KeyA|B
KeyA|B
KeyA|B
KeyA|B
KeyA|B
0
1
1
Never
KeyB
KeyA|B
KeyB
Never
KeyB
1
0
1
Never
Never
KeyA|B
KeyB
Never
Never
1
1
1
Never
Never
KeyA|B
Never
Never
Never
(KeyA|B means key A or key B, Never means that can not be realized under any
conditions)
For example: the block 3, access control bits is C13 C23 C33 = 100, means:
Password A: unreadable, verify KEYB correct, may write (change).
Access control: authentication KEYA or KEYB correctly, readable but can not write
Password B: unreadable, verify KEYB correctly, can write.)
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 FF 07 80 69 B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5










