Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Copyright ©
- Introduction
- At a Glance
- Child Safety
- Safety Belts
- Supplementary Restraints System
- Keys and Remote Controls
- MyKey™
- Locks
- Security
- Steering Wheel
- Wipers and Washers
- Lighting
- Windows and Mirrors
- Instrument Cluster
- Information Displays
- Climate Control
- Seats
- Auxiliary Power Points
- Storage Compartments
- Starting and Stopping the Engine
- Unique Driving Characteristics
- Fuel and Refueling
- Transmission
- Brakes
- Stability Control
- Parking Aids
- Cruise Control
- Driving Aids
- Load Carrying
- Towing
- Driving Hints
- Roadside Emergencies
- Fuses
- Maintenance
- General Information
- Opening and Closing the Hood
- Under Hood Overview
- Under Hood Overview
- Under Hood Overview
- Engine Oil Dipstick
- Engine Oil Dipstick
- Engine Oil Dipstick
- Engine Oil Check
- Engine Coolant Check
- Brake and Clutch Fluid Check
- Washer Fluid Check
- Changing the 12V Battery
- Checking the Wiper Blades
- Changing the Wiper Blades
- Adjusting the Headlamps
- Removing a Headlamp
- Changing a Bulb
- Bulb Specification Chart
- Technical Specifications
- Vehicle Care
- Wheels and Tires
- Capacities and Specifications
- Audio System
- Navigation
- SYNC™
- Appendices
Calculating Fuel Economy
Do not measure fuel economy during the
first 1000 miles (1600 km) of driving (this
is your engine’s break-in period). A more
accurate measurement is obtained after
2000 - 3000 miles (3200 - 4800 km).
Also, fuel expense, frequency of fill ups or
fuel gauge readings are not accurate ways
to measure fuel economy.
1. Fill the fuel tank completely and record
the initial odometer reading.
2. Each time you fill the tank, record the
amount of fuel added.
3. After at least three to five tank fill ups,
fill the fuel tank and record the current
odometer reading.
4. Subtract your initial odometer reading
from the current odometer reading.
5. Calculate fuel economy by dividing
miles traveled by gallons used (For
Metric: Multiply liters used by 100, then
divide by kilometers traveled).
Keep a record for at least one month and
record the type of driving (city or freeway).
This provides an accurate estimate of your
vehicle’s fuel economy under current
driving conditions. Additionally, keeping
records during summer and winter show
how temperature impacts fuel economy.
In general, lower temperatures mean lower
fuel economy.
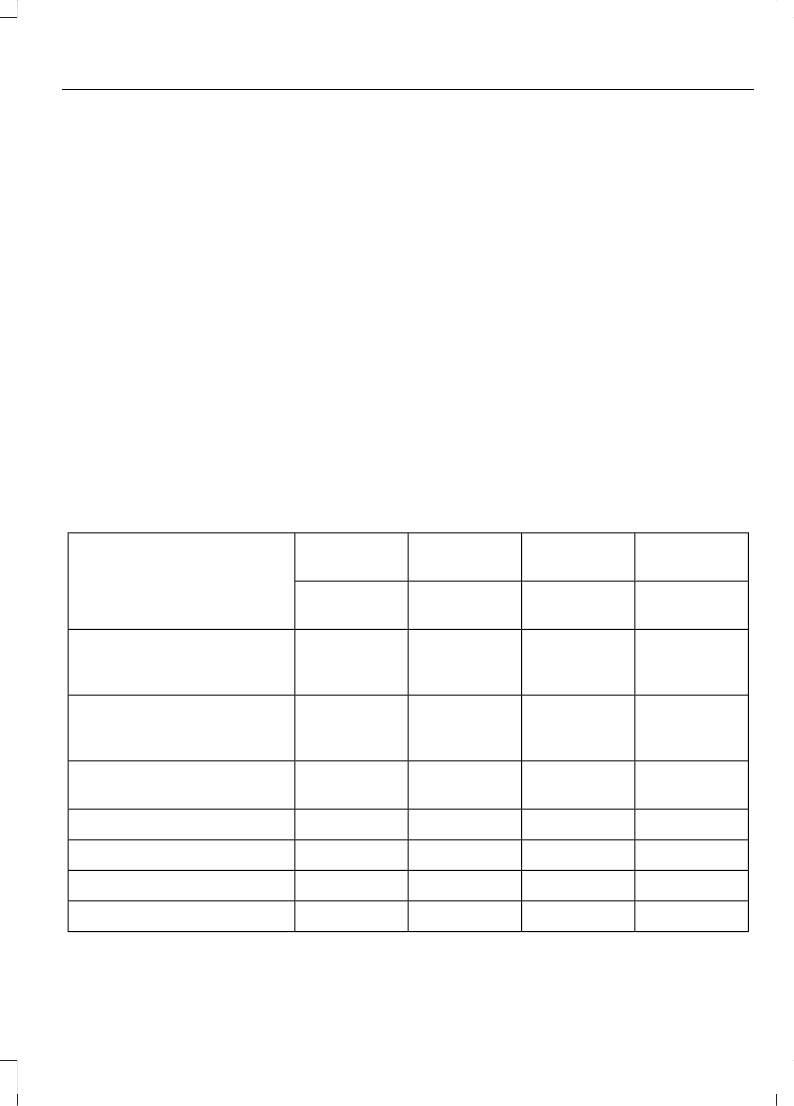
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Fuel Consumption Figures
CO2 Emis-
sions
CombinedExtra-UrbanUrban
Variant
g/km
l/100 km
(mpg)
l/100 km
(mpg)
l/100 km
(mpg)
1195.1 (55.4)4.3 (65.7)6.6 (42.8)
1.0L EcoBoost
(74kW/100PS) without
start-stop
1144.9 (57.6)4.2 (67.3)6 (47.1)
1.0L EcoBoost
(74kW/100PS) with start-
stop
1144.9 (57.6)4.2 (67.3)6 (47.1)
1.0L EcoBoost
(90kW/120PS)
1396 (47.1)4.9 (57.6)7.9 (35.8)1.4L Duratec-16V
1496.4 (44.1)5.1 (55.4)8.6 (32.8)1.6L Duratec-16V Ti-VCT
1044 (70.6)3.6 (78.4)4.7 (60.1)1.5L Duratorq-TDCi
1094.1 (68.9)3.8 (74.3)4.8 (58.9)1.6L Duratorq-TDCi
103
B-MAX (CB2) Vehicles Built From: 25-06-2012, Vehicles Built Up To: 31-12-2013
Fuel and Refueling










