- General Electric Computer Accessories User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Safety Symbol Legend
- Chapter 1 Overview
- Chapter 2 Faults and Troubleshooting
- Chapter 3 Paramters/Functions
- Introduction
- Diagnostic and Utility Functions
- Drive Configuration Functions
- General Setup Functions
- I/O Functions
- LAN Functions
- Motor Control Functions
- Protective Functions
- Custom User Faults
- DC Link Protection
- Ground Fault Protection (Fast)
- Hardware Fault Strings
- Heatsink Thermal Protection
- Line-Line Voltage Protection
- Motor Overtemperature Detection
- Phase Current Protection
- Timed Overcurrent Detection
- Transformer Overtemperature Detection
- Motor Ground Protection
- Phase Imbalance Monitor
- Line Monitor
- Phase Lock Loop
- Sequencer Functions
- Speed Reference Functions
- Speed/Torque Control Functions
- System Data Parameters
- Chapter 4 Wizards
- Introduction
- Introduction 4-1
- DAC Setup
- Drive Commissioning
- Drive Commissioning: Overview
- Drive Commissioning: Intelligent Part Number
- Drive Commissioning: Drive Units
- Drive Commissioning: AC Source Selection
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Nameplate Data
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Crossover Voltage
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Protection Class
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Poles
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Data Sheet
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Data Sheet - Equivalent Circuit Data
- Drive Commissioning: Motor Data Sheet - Flux Curve
- Drive Commissioning: Motor and Process Speed Referencing
- Drive Commissioning: Tachometer Support
- Drive Commissioning: Tachometer Pulses Per Revolution
- Drive Commissioning: Tachometer Loss Protection
- Drive Commissioning: Stopping Configuration
- Drive Commissioning: Flying Restart
- Drive Commissioning: X-Stop Configuration
- Drive Commissioning: X-Stop Ramp Time
- Drive Commissioning: Run Ready Permissive String
- Drive Commissioning: Starting and Stopping the Drive
- Drive Commissioning: Manual Reference
- Drive Commissioning: Maximum Speed References
- Drive Commissioning: Jog Speed Setpoints
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Bypass
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Mode
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Speed Independent Rates
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Speed Independent Rate Set Selection
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Programmed Acceleration Rates
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Programmed Acceleration Speeds
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Programmed Deceleration Rates
- Drive Commissioning: Reference Ramp Programmed Deceleration Speeds
- Drive Commissioning: DDI Increment and Decrement Rates (Local Mode)
- Drive Commissioning: Speed/Torque Regulator Configuration
- Drive Commissioning: Speed/Torque Regulator Modes
- Drive Commissioning: Torque Regulator Reference and Output
- Drive Commissioning: Torque with Speed Override Reference and Output
- Drive Commissioning: Torque with Speed Override Speed Error
- Drive Commissioning: Torque with Speed Override Stopping Behavior
- Drive Commissioning: Torque and Current Limits
- Drive Commissioning: Torque and Current Limits Uniform
- Drive Commissioning: Failed Calculation
- Drive Commissioning: Torque and Current Limit Selection
- Drive Commissioning: Normal Torque and Current Limits
- Drive Commissioning: Alternate Torque and Current Limits
- Drive Commissioning: Motoring Torque Limits
- Drive Commissioning: Generating Torque Limits
- Drive Commissioning: Current Limits
- Drive Commissioning: Power Dip Ride-Through
- Drive Commissioning: Parameter Calculation
- Drive Commissioning: Simulator Mode
- Drive Commissioning: Hardware Fault Strings in Simulator Mode
- Drive Commissioning: Simulator Mechanical Configuration
- Drive Commissioning: Exit Reminder
- Drive Commissioning: Conclusion
- Line Transfer Tuneup
- Motor Control Tuneup
- Panel Meter Setup
- Per Unit Setup
- Line Protection Setup
- Pulse Test
- Remaining Parameter Setup
- Simulator Setup
- Speed Regulator Tuneup
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: Model
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: System Inertia
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: Inertia Measurement Command
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: Speed Regulator Mode
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: Manual Regulator Tuneup
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: 1st Order Response
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: 2nd Order Response
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: 2nd Order Response with Stiffness Filter
- Speed Regulator Tuneup: Calculate Speed Regulator Gains Command
- Notes
- Chapter 5 Signal Mapping
- Appendix A Function Block Diagrams
- Index
- Reader Comments
4-36
•
••
•
Chapter 4 Wizards Innovation Series Medium Voltage GP Type - G Drives GEH-6385
Detailed descriptions of the Park and Pulse states are as follows:
Bridge State Description
Off state
All the power devices in the bridge are turned off. Due to the
nature of the power devices and the topology of the power
circuit any currents which exist in off phases are quickly driven
to zero. Phases not included in the pulse or park state remain in
the off state.
Park state The devices in the bridge are turned on in such a way as to
impress no voltage between the selected drive terminals.
Devices are turned on such that the selected drive terminals are
all connected to the same DC voltage potential within the bridge
(MINUS, ZERO or PLUS). Phases not selected for the park
state are left OFF for the duration of the park state. Phases
listed in the park state and NOT listed in the pulse state will
remain in the park state for the duration of the pulse state. Any
current existing in the power bridge will circulate between the
drive and the load and decay to zero at a rate that depends on
the load electrical time constant.
Pulse state
The devices in the bridge are turned on in such a way as to
impress a voltage between the selected drive terminals and the
terminals left in the park state. Voltage is created using the
devices to connect the pulsed terminals to another internal DC
voltage potential. This condition can lead to rising currents if a
load is connected to the bridge. The total phase-phase voltage
developed is the difference between the internal DC bus
voltages selected for the park and pulse states (MINUS, ZERO,
PLUS).
The Pulse Test user specifies the phases to park and the park state potential by
setting parameters Park phase and Park level to desired values.
The Pulse Test user specifies the phases to pulse and the pulse state potential by
setting parameters Pulse phase and Pulse level to desired values.
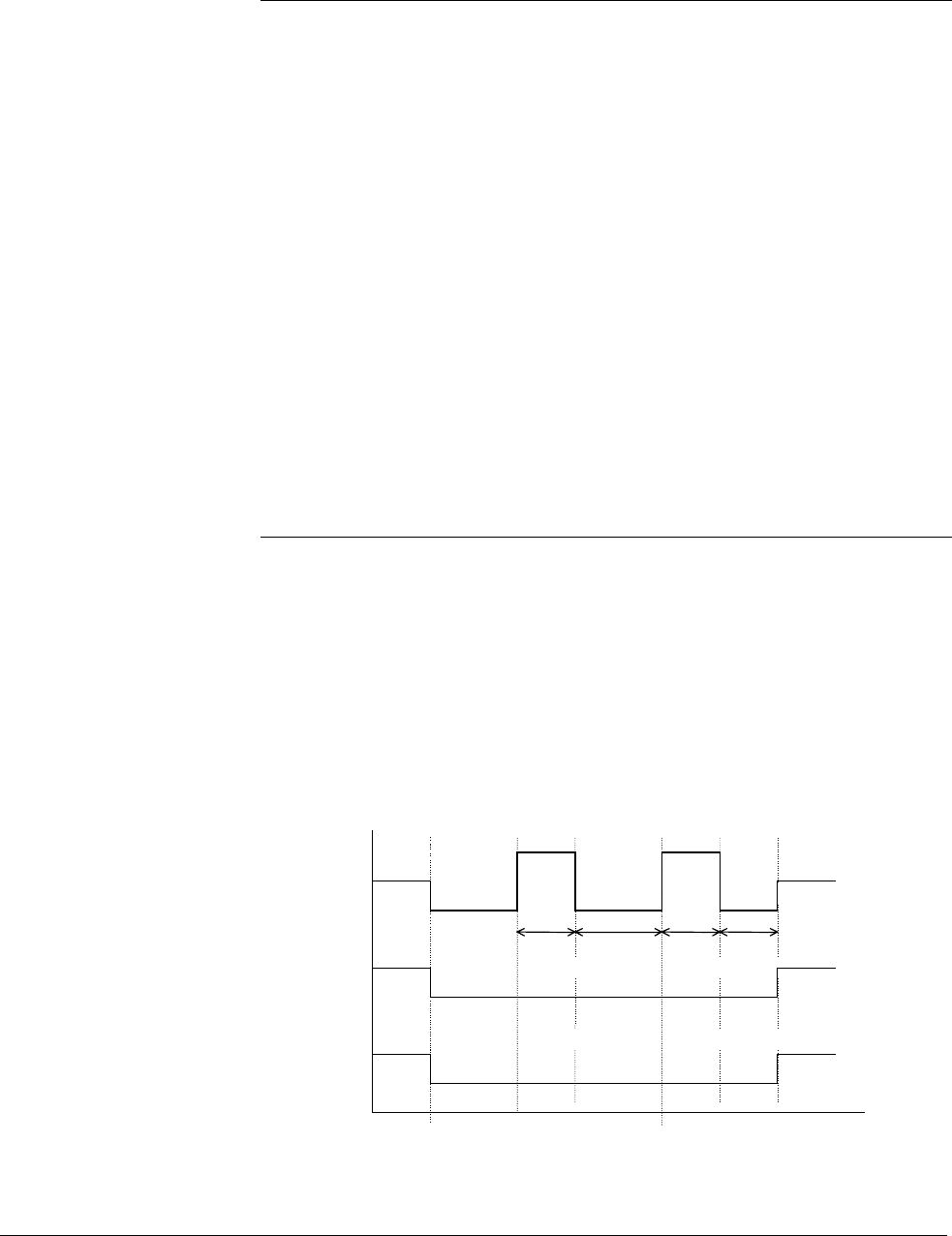
Consider the following example response for parameters set as follows:
Park phase = A, B, C
Park level = MINUS
Pulse phase =A
Pulse level =PLUS
A
B
C
Plus
Plus
Plus
Minus
Minus
Minus
Zero
Zero
Zero
Task 1
load
pulse
Pulse 1
on time
Mid pulse
off time
Pulse 2
on time
Post
pulse off
time
Task 1
load
pulse










