APPENDIX A: TROUBLESHOOTING This chapter provides solutions to frequently encountered problems that can occur during the installation and operation of the 22Mbps Wireless Network PC Card. Please read through the following to solve your problems. 1. The wireless clients cannot access the network in the infrastructure mode. ¾ Check that the wireless network device is being installed and working properly.
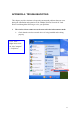
Go to “Hardware” Go to “Device Manager” 22
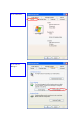
Right mouse click on the wireless network adapter 22Mbps WLAN Adapter Go to “Properties” 22Mbps WLAN Adapter 23
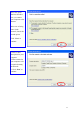
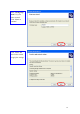
Check and make sure that the network adapter is working properly 22Mbps WLAN Adapter 2. What is the difference between 22Mbps and 11Mbps wireless products? What’s the benefit of 22Mbps Wireless Access Point? The 22Mbps is made possible by the new modulation method called PBCC developed by TI, which is different from the current CCK modulation method for 11Mbps. The 22Mbps Wireless Access Point offers double data rate than that of 11Mbps with 20% more distance coverage.
allows the network to identify it at the hardware level. Unlike IP addresses, which can be changed or dynamically assigned by the network, the MAC address of a networking device is permanent. 5. What is WEP? Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a type of data encryption mechanism described in the IEEE 802.11 standard. The 22Mbps Wireless Access Point supports 64/128/256 bit shared key for WEP. 6. Would the information be transmitted securely in the air? WLAN offers two layers of protection for security.
APPENDIX B: NETWORKING BASIS This chapter will help you learn the basics of home networking.
Select the option that best describes how you connect your computer to the Internet. In the case of using router in the network, choose the second option. Click “Next” to continue. 1. Enter a short description for your computer. 2. Enter a name for your computer to be recognized among the network. 3. Click “Next” to continue.
Enter “Workgroup name” for your home network. Click “Next” to continue” Click “Next” and wait for the wizard to apply the settings.
You may create a network setup disk which saves you the trouble of having to configure every PCs in your network. Select the first choice, and insert a floppy disk into your disk drive Click “Next” to continue.
Click “Format Disk” if you wish to format the disk. Click “Next” to copy the necessary files to the disk.
!Note: Now you may use the Network Setup Disk you just created in any PCs in your network that you wish to setup. Simply insert the Network Setup Disk into the disk drive of a PC, and open to browse the content of the disk with “My Computer” or “Windows File Manager”. Double-click and run the file “netsetup” for the program to handle the rest. Click “Finish” to complete the Network Setup Wizard. System will now have to restart in order for the new settings to be effective.
Checking IP Address of Your Computer In Windows XP Sometimes you will need to know the IP address of the computer that you are using. For example, when you want to make sure that your computer is in the same network domain as that of your Access Point for you can configure and access the AP. Go to Start menu > Run > type “command” Click “OK” When the command prompt window appears, type command “ipconfig /all” and press Enter.
Go to Start menu > Run > type “command” Click “OK” Type command, “ipconfig /renew” in the command prompt window and press Enter. This command releases the current IP address and acquire it from the network, i.e. DHCP server, once more. In this case, the IP address that we acquired is the same as previous one, 192. 168.0.23. However, it’s often that the acquired IP address of the network adapter might would not be the same.
Dynamic IP Address V.S. Static IP Address By definition Dynamic IP addresses are the IP addresses that are being automatically assigned to a network device on the network. These Dynamically assigned IP addresses will expire and may be changed over time. Static IP addresses are the IP addresses that users manually enter for each of the network adapters.
The Local Area Connection Properties would appear. Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” and Click “Properties” to continue. 22Mbps WLAN Adapter Dynamically Assigned IP Address The TCP/IP Properties window appears. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” if you are on a DHCP enabled network.
Static IP Address Select “Use the following IP address” Enter the IP address and subnet mask fields. Enter the IP address of the Router in the Default gateway field. Enter the IP address of the Router in the DNS server field Click “Ok” to close the window !Note: Point.
The TCP/IP Properties window appears. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” if you are on a DHCP enabled network. Click “OK” to close the window with the changes made Select “Use the following IP address” Enter the IP address and subnet mask fields. Enter the IP address of the Router in the Default gateway field.
Wireless Network In Windows 98 and Windows ME Go to Start menu > Settings > Control Panel > Double-click on Network Select TCP/IP of the network device 22Mbps WLAN Adapter Click “Properties” to continue The TCP/IP Properties window appears. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” if you are on a DHCP enabled network.
Select “Use the following IP address” Enter the IP address and subnet mask fields. Enter the IP address of the Router in the Default gateway field.
APPENDIX C: 802.1x Authentication Setup There are three essential components to the 802.1x infrastructure: (1) Supplicant, (2) Authenticator and (3) Server. The 802.1x security supports both MD5 and TLS Extensive Authentication Protocol (EAP). The 802.1x Authentication is a complement to the current WEP encryption used in wireless network. The current security weakness of WEP encryption is that there is no key management and no limitation for the duration of key lifetime. 802.
have access to the Internet/Intranet. In 802.1x authentication infrastructure, each of these wireless clients would have to be authenticated by the Radius server, which would grant the authorized client and notified the Access Point to open up a communication port to be used for the granted client. There are 2 Extensive Authentication Protocol (EAP) methods supported: (1) MD5 and (2) TLS.
Please note that the setup illustration is based on our 22Mbps wireless PC Card. 1. 2. 3. 4. Go to Start > Control Panel double-click on “Network Connections” right-click on the Wireless Network Connection that you use with our 22Mbps wireless PC Card. Click “Properties” to open up the Properties setting window.
5. Click on the “Wireless Network” tab.
6. Click “Properties” of the available wireless network, which you wish to connect or configure. Please note that if you are going to change to a different 802.1x authentication EAP method, i.e. switch from using MD5 to TLS, , you must remove the current existing wireless network from your Preferred networks first, and add it in again. To configure for using TLS authentication method, please follow steps 7 ~ 25. Please follow steps 26 ~ for using MD5 authentication method.
TLS Authentication 7. Select “The key is provided for me automatically” option 8. Click “OK” to close the Wireless Network Properties window.
9. 10. Click “Authentication” tab Select “Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1x” option to enable 802.1x authentication. 11. Select “Smart Card or other Certificate” from the drop-down list box for EAP type. 12. Click “OK” to close the Wireless Network Connection Properties window, thus make the changes effective. The wireless client configuration in the zero-configuration utility provided in Windows XP is now completed for TLS configuration. Before you can enable IEEE 802.
TLS Authentication – Download Digital Certificate from Server In most corporations, it requires internal IT or MIS staff’s help to have the certificated downloaded to your local computer. One of the main reasons is that each corporation uses its own server systems, and you will need the assistance from your IT or MIS for account/password, CA server location and etc.
16. Now we are connected to the Certificate Service. certificate”, and click “Next” to continue.
17. Select “User Certificate request”, and click “Next” to continue.
18. Click “Submit >” to continue.
19. The Certificate Service is now processing the certificate request.
20. The certificate is issued by the server, click “Install this certificate” to download and store the certificate to your local computer. 21. Click “Yes” to store the certificate to your local computer.
22. Certificate is now installed.
All the configuration and certificate download are now complete. Let’s try to connect to the Access Point using 802.1x TLS Authentication. 23. Windows XP will prompt you to select a certificate for wireless network connection. Click on the network connection icon in the system tray to continue.
24. Select the certificate that was issued by the server (WirelessCA), and click “OK” to continue. 25. Check the server to make sure that it’s the server that issues certificate, and click “OK” to complete the authentication process.
MD5 Authentication 26. Select “Data encryption (WEP enabled)” option, but leave other option unselected. 27. Select the key format that you want to use to key in your Network key. ASCII characters: 0~9, a~z and A~Z HEX characters: 0~9, a~f 28. Select the key length that you wish to use 40 bits (5 characters for ASCII, 10 characters for HEX) 104 bits (13 characters for ASCII, 26 characters for HEX) 29. After deciding the key format and key length that you wish to use for network key.
31. 32. Select “Authentication” tab. Select “Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1X” to enable 802.1x authentication. 33. Select “MD-5 Challenge” from the drop-down list box for EAP type. 34. Click “OK” to close Wireless Network Connection Properties window, thus make all the changes effective.
Unlike TLS, which uses digital certificate for validation, the MD-5 Authentication is based on the user account/password. Therefore, you must have a valid account used by the server for validation. 35. WindowsXP will prompt you to enter your user name and password. Click on the network connection icon in the system tray to continue.
36. 37. Enter the user name, password and the logon domain that your account belongs if you have one or more network domain exist in your network. Click “OK” to complete the validation process.
Authenticator: Wireless Network Access Point This is the web page configuration in the Access Point that we use. 1 3 4 5 1. Enable 802.1x security by selecting “Enable”. 2. If MD5 EAP methods is used then you can skip step 3 and go to step 4. 3. Select the Encryption Key Length Size ranging from 64 to 256 Bits that you would like to use. Select the Lifetime of the Encryption Key from 5 Minutes to 1 Day.
!Note: As soon as 802.1x security is enabled, all the wireless client stations that are connected to the Access Point currently will be disconnected. The wireless clients must be configured manually to authenticate themselves with the Radius server to be reconnected.
Radius Server: Window2000 Server This section to help those who has Windows 2000 Server installed and wants to setup Windows2000 Server for 802.1x authentication, which includes setting up Certificate Service for TLS Authentication, and enable EAP-methods. 1. Login into your Windows 2000 Server as Administrator, or account that has Administrator authority. 2. 3. 4.
5. Select “Enterprise root CA”, and click “Next” to continue. 6. Enter the information that you want for your Certificate Service, and click “Next” to continue.
7. 8. 9. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Certificate Authority Right-click on the “Policy Setting”, select “new” Select “Certificate to Issue” 10. Select “Authenticated Session” and “Smartcard Logon” by holding down to the Ctrl key, and click “OK” to continue.
11. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers. 12. Right-click on domain, and select ”Properties” to continue. 13. Select “Group Policy” tab and click “Properties” to continue.
14. Go to “Computer Configuration” > “Security Settings” > “Public Key Policies” 15. Right-click “Automatic Certificate Request Setting”, and select “New” 16. Click “Automatic Certificate Request ...
17. The Automatic Certificate Request Setup Wizard will guide you through the Automatic Certificate Request setup, simply click “Next” through to the last step. 18. Click “Finish” to complete the Automatic Certificate Request Setup 19. Go to Start > Run, and type “command” and click “Enter” to open Command Prompt. 20. Type “secedit/refreshpolicy machine_policy” to refresh policy.
Adding Internet Authentication Service 21. Go to Start > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs 22. Select “Add/Remove Windows Components” from the panel on the left. 23. Select “Internet Authentication Service”, and click “OK” to install.
Setting Internet Authentication Service 24. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Internet Authentication Service 25.
26. Enter the IP address of the Access Point in the Client address text field, a memorable name for the Access Point in the Client-Vendor text field, the access password used by the Access Point in the Shared secret text field. Re-type the password in the Confirmed shared secret text field. 27. Click “Finish” to complete adding of the Access Point.
28. In the Internet Authentication Service, right-click “Remote Access Policies” 29. Select “New Remote Access Policy”. 30. Select “Day-And-Time-Restriction”, and click “Add” to continue.
72
31. Unless you want to specify the active duration for 802.1x authentication, click “OK” to accept to have 802.1x authentication enabled at all times. 32. Select “Grant remote access permission”, and click “Next” to continue.
33.
For TLS Authentication Setup (Steps 34 ~ 38) 34. Select “Authentication” Tab 35.
36. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers 37. Select “Users”, and double-click on the user that can be newly created or currently existing, who will be configured to have the right to obtain digital certificate remotely. Please note that in this case, we have a user called, test, whose account/password are used to obtain the digital certificate from server.
38. Go to the “Dial-in” tab, and check “Allow access” option for Remote Access Permission and “No Callback” for Callback Options.
For MD5 Authentication (Steps 39 ~ 54) 39. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers. 40.
41. Select “Group Policy” tab, and click “Edit” to edit the Group Policy.
42. Go to “Computer Configuration” > “Windows Settings” > “Security Settings” > “Account Policies” > “Password Policies” 43. Click “Define this policy setting”, select “Enabled”, and click “OK” to continue.
44. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers. 45. Go to Users.
46. Go to “Account” tab, and enable “Store password using reversible encryption” 47. Click “OK” to continue.
48. Go to Start > Program > Administrative Tools > Internet Authentication Service. 49. Go to Remote Access Policies 50. Make sure that MD5 is moved up to Order 1 51.
52. Go to “Authentication” tab 53. Enable “Extensible Authentication Protocol” 54. Select “MD5-Challenge” for EAP type.
APPENDIX D: GLOSSARY Access Point ― An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks. Ad-Hoc ― An independent wireless LAN network formed by a group of computers, each with an network adapter. AP Client – One of the additional AP operating modes offered by 22Mbps Access Point, which allows the Access Point to act as an Ethernet-to-Wireless Bridge, thus a LAN or a single computer station can join a wireless ESS network through it.
Beacon ― A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Access Point to keep the network synchronized. Included in a beacon are information such as wireless LAN service area, the AP address, the Broadcast destination addresses, time stamp, Delivery Traffic Indicator Maps, and the Traffic Indicator Message (TIM). Bit ― A binary digit, which is either -0 or -1 for value, is the smallest unit for data. Bridge ― An internetworking function that incorporates the lowest 2 layers of the OSI network protocol model.
retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears as low power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband receivers. Dynamic IP Address ― An IP address that is assigned automatically to a client station in a TCP/IP network by a DHCP server. Encryption ― A security method that uses a specific algorithm to alter the data transmitted, thus prevent others from knowing the information transmitted. ESS ― ESS stands for “Extended Service Set”.
bandwidth for unlicensed use in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4GHz, in particular, is being made available worldwide. MAC Address ― Media Access Control Address is a unique hex number assigned by the manufacturer to any Ethernet networking device, such as a network adapter, that allows the network to identify it at the hardware level. Multicasting ― Sending data to a group of nodes instead of a single destination.
SSID ― Service Set Identifier, which is a unique name shared among all clients and nodes in a wireless network. The SSID must be identical for each clients and nodes in the wireless network. Subnet Mask ― The method used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP address to turn part of the host ID address field into a field for subnets. TCP/IP ― Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol.
APPENDIX E: TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Standard Data Rate Emission Type Data Modulation 802.11b compliant (wireless) 1 / 2 / 5.5 / 11 / 22 Mbps Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) 1 Mbps – BPSK 2 Mbps – QPSK 5.5 / 11 Mbps – CCK 5.