user manual
T
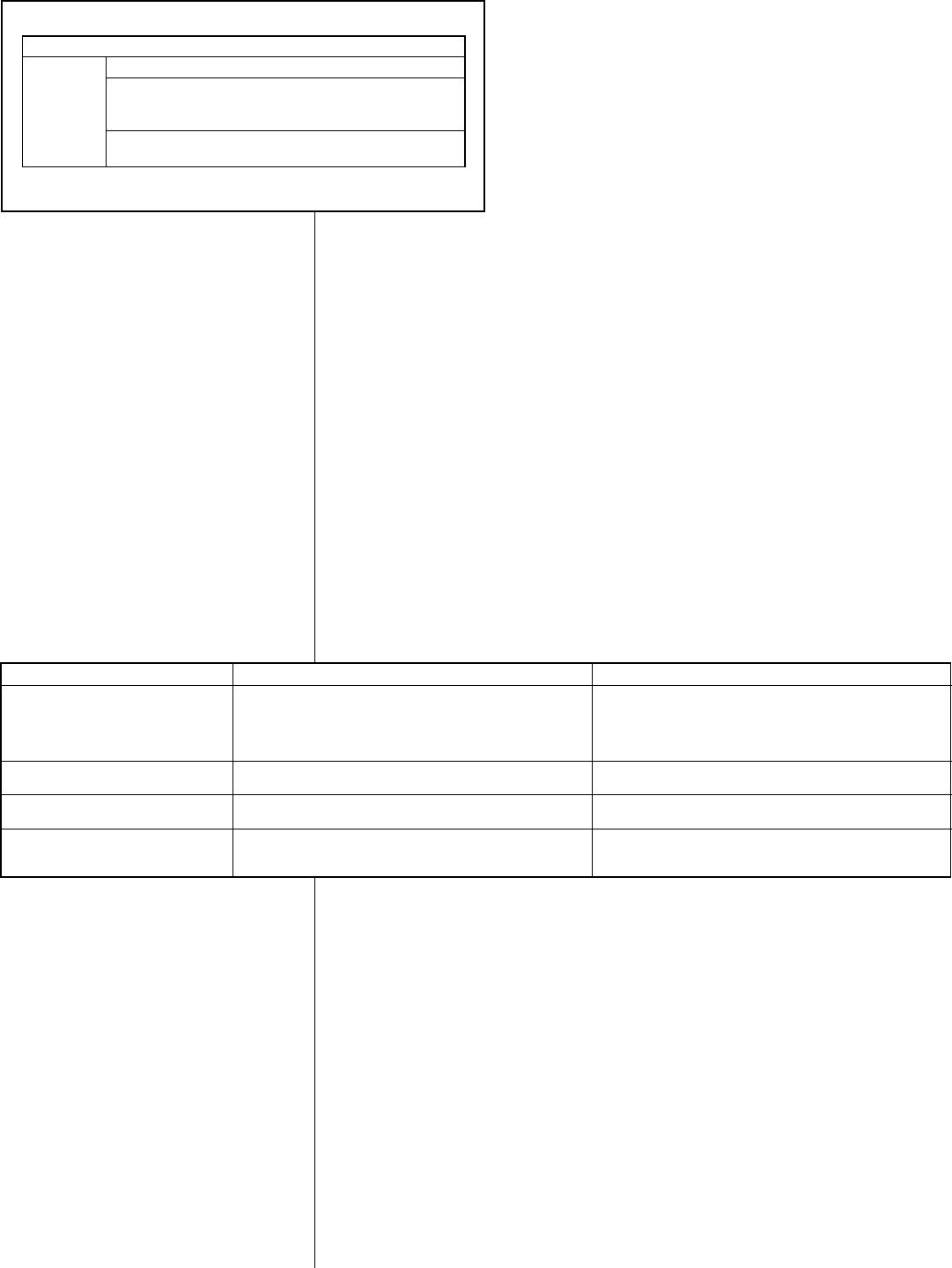
ABLE 5
16
(1) Wire length equals twice the run distance.
FIELD WIRE SIZE FOR 24 VOLT THERMOSTAT CIRCUITS
SOLID COPPER WIRE - AWG
3.0 16 14 12 10 10 10
2.5 16 14 12 12 10 10
2.0 18 16 14 12 12 10
50 100 150 200 250 300
Length of Run - Feet (1)
Thermostat
Load - Amps
N
OTE: The condensing unit is shipped with a holding charge of dry nitrogen
which must be purged from the unit before evacuation.
1. Since the condensing unit itself must be evacuated, open the suction, discharge and
l
iquid shut-off valves.
2. Use a refrigeration type vacuum pump capable of evacuation in the 500 micron
range.
3. Connect the vacuum pump to the service manifold assembly with a pressure gauge
that will read 30 inches vacuum. Connect the service manifold to the suction line
schrader valve port.
4. With an accurate scale,
1
⁄2 oz., set refrigerant tank up so its weight can be measured
while in a position to charge liquid. (Unit must be off.) Energize liquid line solenoid
valve by wiring valve to 24V power supply (or open by manual stem if applicable).
5. Connect to the liquid shut-off valve port. Shut off tank and evacuate the system. The
pressure gauge should read at least 29.5" of vacuum.
6. Triple evacuate the system.
7. The refrigerant system will now be free of noncondensables.
8. Remove vacuum pump from 3-way valve.
9. Before tightening, purge tank and service valve hose.
10. Note weight of refrigerant tank.
11. De-energize liquid line solenoid valve. Open refrigerant tank valve. Allow pressure in
tank and unit to equalize.
12. Close off service valve to liquid port and note weight of refrigerant tank.
13. Re-wire liquid line solenoid to thermostat control. Close main disconnect switch and
turn thermostat to lowest setting.
14. Charge unit per chart.
SYMPTOM
POSSIBLE CAUSE REMEDY
High head pressure a. Air flow to or from condenser restricted or a. Remove obstruction, relocate condensing unit,
dirty condenser if necessary clean condenser.
b. Faulty condenser fan or motor. b. Replace.
c. Overcharge of refrigerant c. Reduce charge.
d. Air in system. d. Evacuate and recharge.
Low head pressure a. Short of refrigerant. a. Check for leak, add charge.
b. Low evaporator air flow. b. Increase blower speed, check filters.
Low vapor & a. Short of refrigerant. a. Check for leak—add refrigerant.
hot compressor
Excessive sweating a. Low indoor airflow a. Increase speed of air handler blower or reduce
restriction—replace air filter.
b. Excess refrigerant b. Slowly reduce charge.
CHARGING HINTS