Product Overview
Table Of Contents
V4043A,B,E,J; V4044A,B; V8043A,B,E,F,J; V8044A,B,E MOTORIZED VALVES
60-2133—9
8
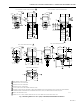
Fig. 2. Maximum temperature characteristics of valves with Class F motors.
EXAMPLE: 150°F (66°C) IS THE AMBIENT TEMPERATURE AT THE VALVE,
235°F (113°C) IS MAXIMUM FLUID TEMPERATURE.
MAXIMUM AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE LINE
MAXIMUM FLUID
TEMPERATURE
LINE
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
FLUID TEMPERATURE
M8164
210
(99)
200
(93)
190
(88)
180
(82)
170
(77)
160
(71)
150
(66)
140
(60)
130
(54)
120
(49)
110
(43)
100
(38)
90
(32)
80
(27)
DEGREES F
DEGREES C
70
(21)
80
(27)
90
(32)
100
(38)
110
(43)
120
(49)
130
(54)
140
(60)
150
(66)
160
(71)
170
(77)
180
(82)
190
(88)
200
(93)
210
(99)
220
(104)
230
(110)
240
(116)
250
(121)
How to Find Valve Pressure Drop
The pressure drop in psi (kPa), equivalent ft (m) of pipe, or
feet of water (kPa) can be calculated from Fig. 3 through 8
as follows:
쐃 Calculate the flow rate to heat the zone.
쐇 Determine the C
v
(kV) rating of the motorized valve.
쐋 Select the graph corresponding to the C
v
(kV) rating
(Fig. 3 through 8).
쐏 Determine the pressure drop across the valve using
the following procedures for calculating pressure drop.
Pressure Drop in psi (kPa)
쐃 Locate the flow rate at the bottom of the graph.
쐇 Draw a line up from the flow rate to the intersection of
the curve.
쐋 Draw a line from the intersection to the left edge of the
graph to determine the pressure drop in psi (kPa).
Pressure Drop in Equivalent ft (m) of Pipe
NOTE: Both 1/2 and 3/4 in. pipe conversion scales are
available for this determination.
쐃 Locate the flow rate at the bottom of the graph.
쐇 Draw a line vertically to the top of the graph.
Determine the pressure drop for either the 1/2 or 3/4
in. pipe.
Pressure Drop in ft of Water (kPa)
쐃 Locate the flow rate at the bottom of the graph.
쐇 Draw a line up from the flow rate to the intersection of
the curve.
쐋 Draw a line from the intersection to the right edge of
the graph to determine pressure drop in ft of water
(kPa).