Application Guide
63-706235
VFD Features
— Soft Start: Reduced starting current and avoids pressure surges.
— Motor Speed Low Limit: Minimum air movements levels programmable.
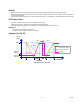
Cooling Tower Fans (See Fig. 41)
EMC
Honeywell
T
Evaporator
Evaporator
Condenser
Chilled Water
Chilled Water
System
System
Condenser Water
Condenser Water
System
System
Cooling Tower
Controller
Controller
Inverter
Inverter
Bypass Valve
Bypass Valve
M
RST
PG
MONPARREFBTNS
RUNREADY FAULT
Honeywel
l
Fig. 41. Application diagram.
Application Description
A chilled water system is made of three main elements: refrigeration unit (water chiller), chilled water distribution network, and a
means of dissipating heat collected by the system. The towers dissipate this collected heat by cooling the condenser water.
The cooling effect in evaporative type cooling towers is dependent on the ratio of water to air contact and wet bulb temperature.
Traditionally when the condenser water is flowing fully over the tower the fan or fans are cycled on and off to control the water
temperature. Partial load operating characteristics have a strong influence on operating costs. As most operation is at less than
design load, fitting a VFD and varying the speed of the fan is a far more efficient means of controlling the condenser water
temperature. For maximum chiller efficiency the condenser water temperature should be as low as can be used by the
refrigeration system dependent on outdoor air conditions (i.e. wet bulb temperature).
When outside air wet bulb temperature is lower than design, the tower can cool water to a lower temperature, (but can never
reach the actual wet bulb temperature). Therefore, the controller setpoint should be at the lowest setpoint attainable (by the
tower) to save chiller energy and not waste fan energy trying to reach an unobtainable value.
Benefits
— Reduced wear and tear.
— Improved control (straight line)—more stable chiller operation.
— Fewer start/stops.
— Energy saving.