user manual
Operating the Analyzer
January 2009 UDA2182 Universal Dual Analyzer Product Manual 37
5.9 Cation Calc Display
5.9.1 Overview
This group allows you to configure dual conductivity inputs for cation or degassed CO
2
measurement. The cation selection of Ammonia or Amines will display a calculated pH
value from differential conductivity and provide continuous pH monitoring using
reliable, maintenance free conductivity cells. An outline of the conductivity cells’
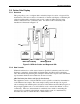
installation is illustrated in Figure 5-6.
Inlet
Flow
Valve
Flow
Meter
Gasses
Cell
#1
Cell
#2
Cell
#3
Cation Exchange Column
Reboiler
Specific
Conductivity
From Cell #1
Cation
Conductivity
From Cell #2
Degassed
Conductivity
From Cell #3
Drain
UDA for Cation Conductivity UDA for Degassed CO
2
Inlet
Flow
Valve
Flow
Meter
Gasses
Cell
#1
Cell
#2
Cell
#3
Cation Exchange Column
Reboiler
Specific
Conductivity
From Cell #1
Cation
Conductivity
From Cell #2
Degassed
Conductivity
From Cell #3
Drain
UDA for Cation Conductivity UDA for Degassed CO
2
Inlet
Flow
Valve
Flow
Meter
Gasses
Cell
#1
Cell
#2
Cell
#3
Cation Exchange Column
Reboiler
Specific
Conductivity
From Cell #1
Cation
Conductivity
From Cell #2
Degassed
Conductivity
From Cell #3
Drain
UDA for Cation Conductivity UDA for Degassed CO
2
Figure 5-6 UDA for Cation and Degassed CO
2
5.9.2 How it works
UDA2182 will monitor on-line treated water for Specific Conductivity and Cation bed
discharge conductivity, using reliable and maintenance free Honeywell conductivity
cells, and calculate the pH, using the assumption that the water is pure water with Amine
type treatment chemical and residual trace un-removed salts.
pH Calculation from Cation and Specific Conductivity
The equipment consists of Cell #1 which is used for specific conductivity determination
of the influent water sample. The water sample is then passed through a strong acid
cation exchange resin which replaces all cations in the influent stream with hydrogen ion.
On passing though the resin, a second Cell #2 is used to measure the effluent or cation
conductivity. These two measurements in combination are useful for measuring the
amount of base contained in the influent sample and the extent of contamination by
unwanted salts such as sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, etc.