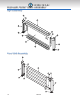
Parts List
24
RM-26
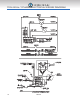
THE REFRIGERATION CYCLE
1. As the temperature inside the cooling compartment increases, it is detected by the thermostats’
sensor. The thermostat then turns the compressor and the condenser motor on once the
programmed temperature is reached.
2. The compressor recirculates the refrigerant throughout the system by drawing the refrigerant gas
at a low vapor pressure from the evaporator. Then it compresses the refrigerant and forces it
into the condenser.
3. The condenser, with the help of its fan motor, removes the refrigerants’ heat as its ows through
the condenser. The heat is then released to the outside environment. Consequently, the decrease
in temperature will change the refrigerant from a gaseous to a liquid state.
4. The capillary tube regulates the amount of refrigerant that is discharged into the evaporator and
expands it. This expansion causes the refrigerant temperature to decrease.
5. The evaporators' serpentine allows the refrigerant to absorb and remove heat from the cooling
compartment.
6. The drop in temperature inside the cooling compartment is caused by the refrigerant’s continuous
circulation through the system. This gas continuously absorbs the heat that exists inside the
cooling compartment and expels it to the outside environment. When the temperature drops to
its programmed set point, it is detected by the thermostat and it turns o the compressor and
condenser motor.