HP Thin Clients Flash/SSD Selection Technical white paper
3
Comparing flash storage devices, uMLC option to hard disk drives
Use the following table to compare the capacity and price of solid-state drives based on SLC flash memory, MLC flash
memory, uMLC flash memory, and a typical 500 GB hard-disk drive (HDD).
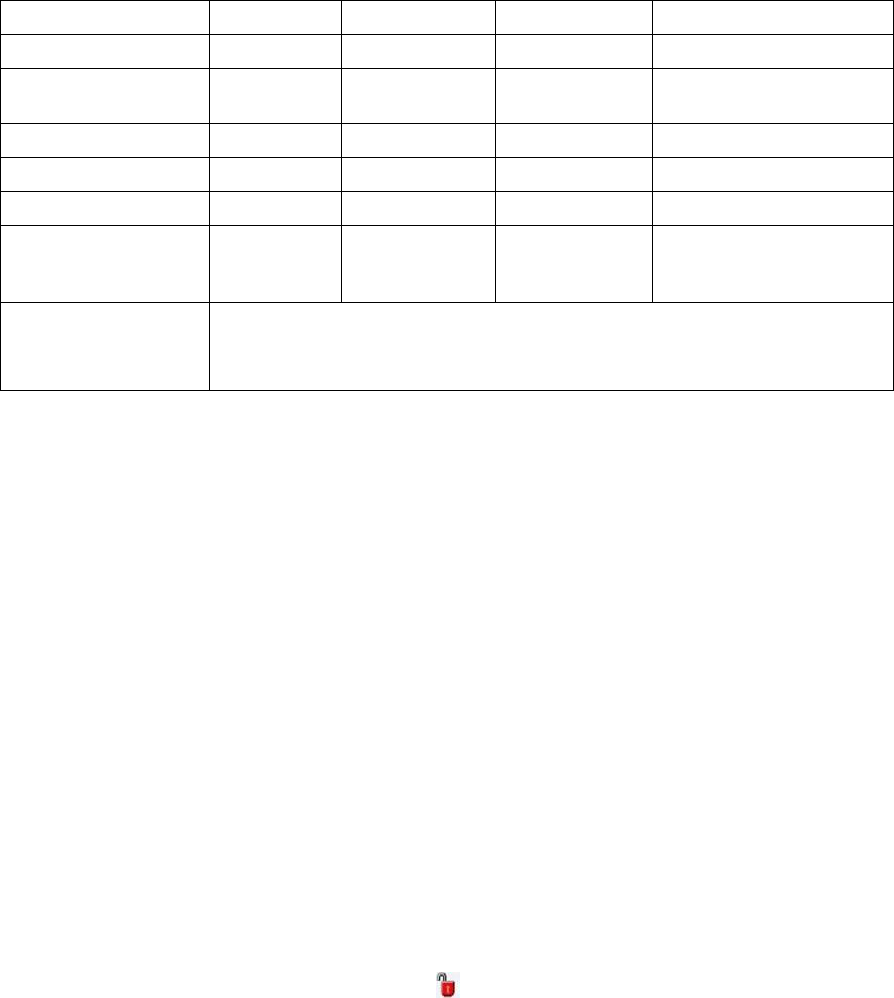
SSD types used in thin clients compared to hard-disk drives (HDDs)
SSD – Data Points
SLC*
MLC*
uMLC**
500 GB HDD 7200 rpm***
Bits per cell
1
2
2 (only 1 is used)
n/a
Program/erase cycles (2x
nm)
60000–100000
3000
15000
n/a
Read time
25 us
50 us
50 us
~11000–15400 us (non-cached)
Program time
200–300 us
600–900 us
600–900 us
~7200–9200 us
Erase time
1.5–2 ms
3–5 ms
3–5 ms
n/a
Estimated retail cost for 16
GB as of November 2014
(unless noted)
~$300+
$69–79
$109-119
$109–149 (500 GB)
* Source: Anandtech.com, Nov. 16, 2012, Samsung SSD 840: Testing the Endurance of TLC NAND
** Source: Phison Electronics Corp.
*** Source: TomsHardware.com, 2013, All 2013 Mobile HDD Charts
It important to consider how long the thin client product will be used in your environment. For example, if the product will be
operated with either File-Based Write Filter or Disabled Write Filter, the storage solution recommended would be uMLC,
higher capacity MLC, and/or hard-disk drive (HDD).
Storage requirements
If the thin clients run with Disabled Write Filter or use the File-Based Write Filter allowing local applications to write to the
SSD, you should thoroughly monitor the flash drive erase count of worst case usage models in your environment to help
determine your highest needs. For effective sampling, monitor a variety of the highest use-case deployments for a period of
a few weeks (200 or more hours) under normal configuration, considering any planned operating system transitions, local
installations, and platform requirements. This method evaluates the storage requirements needed to meet the operational
demands of the deployment in a worst-case scenario. Any planned deployments without the write filter enabled and/or
heavy operation (24/7) writing to the SSD are more likely to need a larger flash memory device, uMLC, or a spinning hard
drive solution. Contact HP Support for assistance in reviewing your deployment.
HP recommendations
HP recommends the following based on your usage environment and operating conditions:
• Typical thin client environments using the Enhanced Write Filter and do not expect extremely frequent operating system
changes and/or re-imaging can select the standard storage offered which is MLC flash memory.
• Thin client environments that expect frequent or regular operating system changes must confirm that their usage model
is within the capabilities of the flash memory device selected. If the amount of write activity increases, a different type of
flash memory or a higher capacity storage device may be needed.
• If the write filter is disabled in the thin client environment ( ) or if File-Based Write Filter permitting writing to local
storage is used, HP recommends confirming that the usage model is verified to be within the specified capabilities of the
local flash device or follow the recommendations in the table below.
• Standard HP Linux image deployments are typically highly virtualized and are well supported by the standard flash
solution. No changes or review is recommended unless there is a custom application regularly writing to system’s flash.





