Reference Guide
Table Of Contents
- Notebook tour
- HP Write Filters
- Configuration
- Applications
- Pointing devices and keyboard
- Using pointing devices
- Using the keyboard
- Using hotkeys
- Displaying system information
- Decreasing screen brightness
- Increasing screen brightness
- Switching the screen image
- Muting speaker sound
- Decreasing speaker sound
- Increasing speaker sound
- Playing the previous track or section of an audio CD or a DVD
- Playing, pausing, or resuming an audio CD or a DVD
- Playing the next track or section of an audio CD or a DVD
- Using hotkeys
- Using the keypads
- Power
- Power control and light locations
- Shutting down the computer
- Setting power options
- Using battery power
- Using external AC power
- Multimedia
- Wireless
- Modem and LAN
- Security
- Connecting hardware
- Using Media Card Reader cards
- Using ExpressCards
- Hardware upgrades
- MultiBoot
- Computer Setup
- Routine care
- Index
NOTE: To use the WLAN device in your computer, you must connect to a WLAN infrastructure
(provided through a service provider or a public or corporate network).
Computers with WLAN devices support one or more of the following IEEE industry standards:
● 802.11a supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 5 GHz.
●
802.11b, the first popular standard, supports data rates of up to 11 Mbps and operates at a
frequency of 2.4 GHz.
● 802.11g supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. An
802.11g WLAN device is backward compatible with 802.11b devices, so they can operate on the
same network.
● 802.11n supports data rates of up to 600 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 2.4 and/or 5 GHz.
An 802.11n WLAN device is backward compatible with 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g devices,
so they can operate on the same network.
Setting up a WLAN
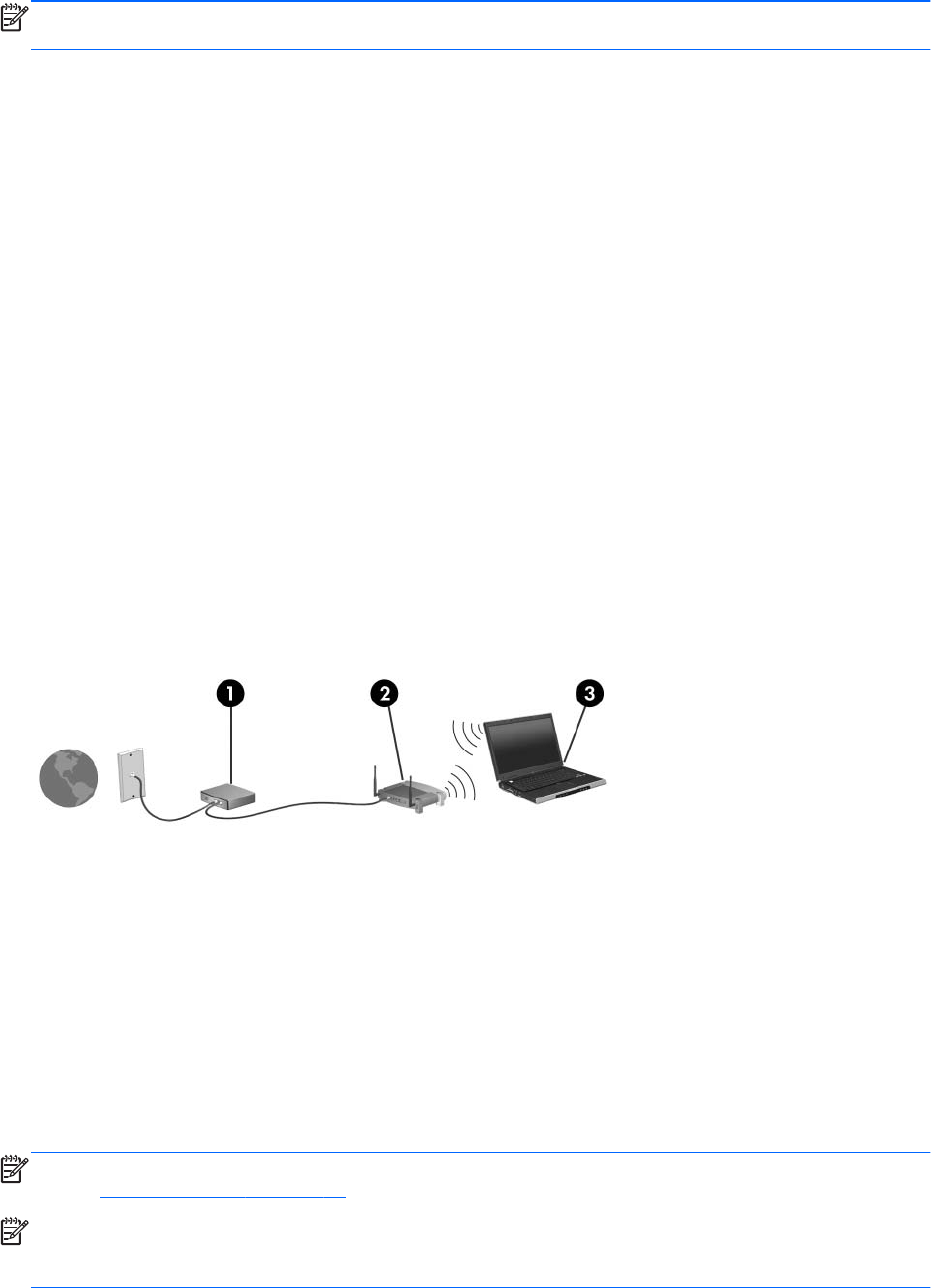
To set up a WLAN and connect to the Internet, you need the following equipment:
● A broadband modem (either DSL or cable) (1) and high-speed Internet service purchased from
an Internet service provider (ISP)
●
A wireless router (purchased separately) (2)
● The wireless computer (3)
The following illustration shows an example of a wireless network installation that is connected to the
Internet.
As your network grows, additional wireless and wired computers can be connected to the network to
access the Internet.
For help in setting up your WLAN, refer to the information provided by your router manufacturer or
your ISP.
Connecting to a WLAN
To connect to a WLAN, follow these steps:
1. Verify that the WLAN device is turned on. If it is on, the wireless light is white. If the wireless light
is amber, press the wireless button.
2. Open Network Connections by selecting Start > Control Panel> Network and Sharing Center.
NOTE: You must commit these changes in order for them to be saved. For additional information,
refer to
HP Write Filters on page 11.
NOTE: The functional range (how far your wireless signals travel) depends on WLAN
implementation, router manufacturer, and interference from other electronic devices or structural
barriers such as walls and floors.
40 Chapter 8 Wireless










