HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.0.0 Fabric Watch User Guide (AA-RW1TA-TE, May 2005)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- About this guide
- An introduction to Fabric Watch
- Fabric Watch concepts
- Fabric watch components
- Configuring events
- Port persistence
- Notification methods
- Switch policies
- Interpreting event messages
- Activating and accessing Fabric Watch
- Configuring Fabric Watch
- Configuring Fabric Watch thresholds
- Configuring notifications
- Configuring switch status policy
- Configuring FRUs
- Configuring Fabric Watch using Web Tools
- Configuring Fabric Watch using SNMP
- Generating Fabric Watch reports
- Default threshold values
- Basic Fabric Watch configuration guidelines
- Using Fabric Watch with configuration files
- Glossary
- Index
23Fabric OS 5.0.0 Fabric Watch user guide
Areas
While classes represent large groupings of information, areas represent the information that
Fabric Watch monitors. For example, switch temperature, one of the values tracked by Fabric
Watch, is an area within the class Environment.
The tables in this section describe all of the areas monitored by Fabric Watch, organized by
their associated classes.
Environment class areas
Table 4 lists and describes the Fabric Watch areas in the Environment class.
Fabric class areas
Table 5 lists Fabric Watch areas in the Fabric class and describes each area.
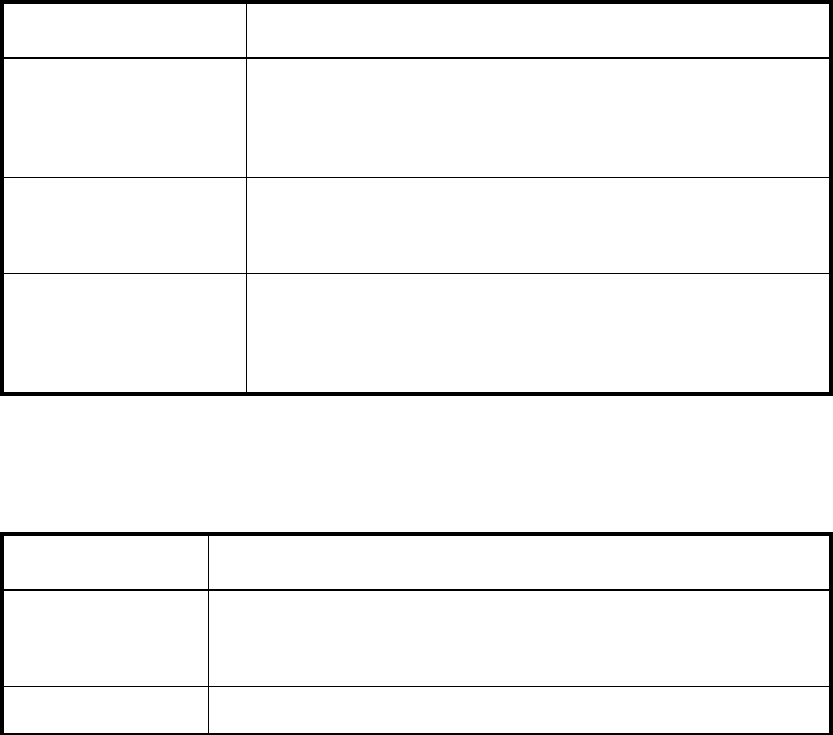
Table 4 Environment class areas
Area Description
Fan Refers to the speed of the fans inside the switch, in revolutions per
minute. It is important that the fans spin quickly enough to keep
the ambient temperature from rising to levels at which switch
damage might occur.
Power Supply Monitors whether power supplies within the switch are on, off,
present, or absent. Fabric Watch monitors power supplies to be
sure that power is always available to a switch.
Temperature Refers to the ambient temperature inside the switch, in degrees
Celsius. Temperature sensors monitor the switch in case the
temperature rises to levels at which damage to the switch might
occur.
Table 5 Fabric class sreas
Area Description
Domain ID Changes Monitors forcible domain ID changes. Forcible domain ID changes
occur when there is a conflict of domain IDs in a single fabric and the
principal switch has to assign another domain ID to a switch.
Fabric Logins Occurs when ports and devices initialize with the fabric.










