HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.0.0 Fabric Watch User Guide (AA-RW1TA-TE, May 2005)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- About this guide
- An introduction to Fabric Watch
- Fabric Watch concepts
- Fabric watch components
- Configuring events
- Port persistence
- Notification methods
- Switch policies
- Interpreting event messages
- Activating and accessing Fabric Watch
- Configuring Fabric Watch
- Configuring Fabric Watch thresholds
- Configuring notifications
- Configuring switch status policy
- Configuring FRUs
- Configuring Fabric Watch using Web Tools
- Configuring Fabric Watch using SNMP
- Generating Fabric Watch reports
- Default threshold values
- Basic Fabric Watch configuration guidelines
- Using Fabric Watch with configuration files
- Glossary
- Index
Fabric Watch concepts30
SFP class areas
Table 11 lists Fabric Watch areas in the SFP class and describes each area.
Elements
Fabric Watch defines an
element
as any fabric or switch component that the software
monitors. Within each area, there are a number of elements equivalent to the number of
components being monitored. For instance, in the Core Switch 2/64, each area of the Port
class will include 64 elements.
Each element contains information pertaining to the description suggested by the area. To
continue the Ports example, each element in the Invalid word area of Ports would contain
exactly 64 ports, each of which would contain the number of times invalid words had been
received by the port over the last time interval. Each of these elements maps to an index
number, so that all elements can be identified in terms of class, area, and index number. As
an example, the monitoring of the temperature sensor with an index of one may be viewed by
accessing the first temperature sensor within the temperature area of the environment class.
Subclasses are a minor exception to the above rule. Subclasses, such as E_Ports, contain
areas with elements equivalent to the number of valid entries. Within the same example used
thus far in this section, in a 64-port switch in which eight ports are connected to another
switch, each area within the E_Port class would contain eight elements.
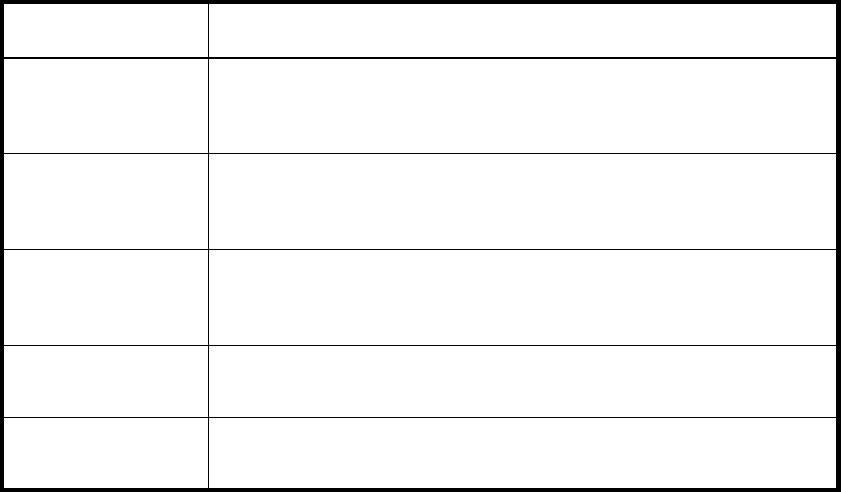
Table 11 SFP class areas
Area Description
Temperature The temperature area measures the physical temperature of the SFP, in
degrees Celsius. A high temperature indicates that the SFP might be in
danger of damage.
Receive Power The receive power area measures the amount of incoming laser, in
µwatts, to help determine if the SFP is in good working condition. If the
counter often exceeds the threshold, the SFP is deteriorating.
Transmit Power The transmit power area measures the amount of outgoing laser, in
µwatts. Use this to determine the condition of the SFP. If the counter
often exceeds the threshold, the SFP is deteriorating.
Current The current area measures the amount of supplied current to the SFP
transceiver. Current area events indicate hardware failures.
Supply Voltage The supply voltage area measures the amount of voltage supplied to
the SFP. If this value exceeds the threshold, the SFP is deteriorating.










