HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.0.0 Fabric Watch User Guide (AA-RW1TA-TE, May 2005)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- About this guide
- An introduction to Fabric Watch
- Fabric Watch concepts
- Fabric watch components
- Configuring events
- Port persistence
- Notification methods
- Switch policies
- Interpreting event messages
- Activating and accessing Fabric Watch
- Configuring Fabric Watch
- Configuring Fabric Watch thresholds
- Configuring notifications
- Configuring switch status policy
- Configuring FRUs
- Configuring Fabric Watch using Web Tools
- Configuring Fabric Watch using SNMP
- Generating Fabric Watch reports
- Default threshold values
- Basic Fabric Watch configuration guidelines
- Using Fabric Watch with configuration files
- Glossary
- Index
35Fabric OS 5.0.0 Fabric Watch user guide
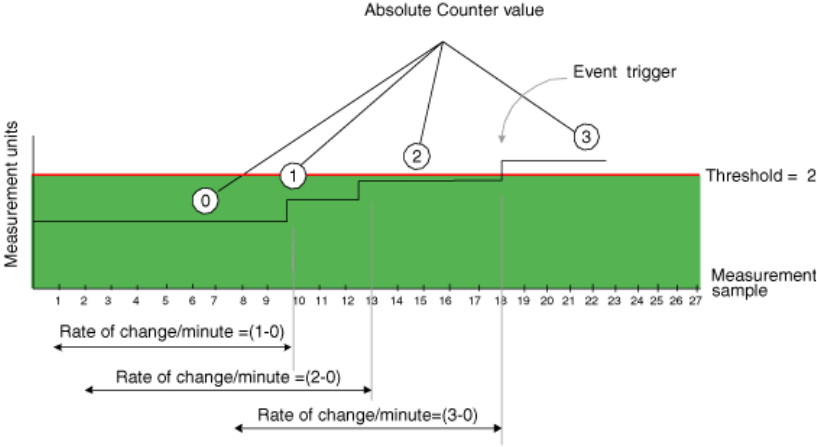
Example1: Triggering an Event
Figure shows a sample graph of data obtained by Fabric Watch (the type of data is
irrelevant to the example). A high threshold of 2 is specified to trigger an event. A time base
of
minute
is defined. An event occurs only if the rate of change in the specific interval (one
minute in this example) is across the threshold boundary. It should be either higher than the
high threshold limit or lower than the low threshold limit. As illustrated on the tenth sample, the
counter value changes from 0 to 1; hence calculated rate of change is 1 per minute. At the
thirteenth sample, the rate of change is 2 per minute. The rate of change must be at least 3
per minute to exceed the event-triggering requirement of 2, which is met on the eighteenth
sample.
Figure 4 Event trigger
Example 2: Not Triggering an Event
Figure uses the same data to illustrate a case in which a threshold is exceeded without
triggering an event. In this case, the calculated rate of change in the data value is always less
than or equal to the high threshold of 2. At the tenth sample, the rate of change is one per
minute. At the fourteenth, twenty-first, and twenty-fifth sample, the rate of change remains










