AHCI and RAID on HP Elite 8100 Business PCs
14
RAID 5 with three hard drives
RAID 5 has been used in servers for many years and is one of the most common types of RAID. RAID 5
uses striping with parity data in distributed blocks across all member disks. Therefore, the mass storage
controller can simultaneously write new information to two hard drives and parity information to the third
hard drive, so if one hard drive fails, the RAID controller can rebuild all the information after the volume
degradation occurred. Hence, RAID 5 with three hard drives has similar performance to RAID 0 with two
hard drives, and the reliability of RAID 1 with a minimum of three hard drives.
Table 4 RAID 5 with 3 hard drives (Parity)
In the previous table, each “Data Segment x” represents a strip. A stripe is made with strip “Data Segment
x”, “Data Segment y” and strip “Parity for x and y.” Notice that the strip “Parity for x and y” is used to
store the required information to recreate the data if any one of the RAID volume members is compro-
mised.
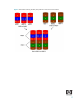
To better illustrate the concept of RAID 5 (parity based RAID), the following figure shows how a sequence
of data “ABCD...” is stored in a RAID 5. In this example, each letter represents a segment or strip. The fig-
ure shows how the various pieces of the information go to different hard drives, hence if any one member
of the RAID 5 fails, the information from all members is not lost.
First Disk Second Disk Third Disk
Data Segment 1 Data Segment 2 Parity for 1 and 2
Data Segment 3 Parity for 3 and 4 Data Segment 4
Parity for 5 and 6 Data Segment 5 Data Segment 6
Data Segment 7 Data Segment 8 Parity for 7 and 8
Data Segment 9 Parity for 9 and 10 Data Segment 10
P a r i t y f o r 11 a n d 12 D a t a S e g m e n t 11 D a t a S e g m e n t 12
D a t a S e g m e n t 13 D a t a S e g m e n t 14 Pa r i t y f o r 13 a n d 14
D a t a S e g m e n t 15 Pa r i t y f o r 15 a n d 16 D a t a S e g m e n t 16
Pa rit y for 17 a n d 18 Dat a S e g m e n t 17 D a t a S e g m e n t 18