Brocade Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator's Guide v6.1.2_cee (53-1001258-01, June 2009)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- About This Document
- Introducing FCoE
- Using the CEE CLI
- In this chapter
- CEE CLI configuration guidelines and restrictions
- Using the CEE command line interface (CLI)
- CEE CLI RBAC permissions
- Accessing the CEE CLI through the console interface or through a Telnet session
- Accessing the CEE CLI from the Fabric OS shell
- Accessing CEE CLI command modes
- Using CEE CLI keyboard shortcuts
- Displaying CEE CLI commands and command syntax
- Using CEE CLI command completion
- CEE CLI command syntax conventions
- Using CEE CLI command output modifiers
- Configuring VLANs Using the CEE CLI
- In this chapter
- VLAN overview
- Ingress VLAN filtering
- VLAN configuration guidelines and restrictions
- Default VLAN configuration
- VLAN configuration procedures
- Enabling and disabling a CEE interface
- Configuring the MTU on a CEE interface
- Creating a VLAN interface
- Configuring a VLAN interface to forward FCoE traffic
- Configuring a CEE interface as a Layer 2 switch port
- Configuring a CEE interface as an access interface or a trunk interface
- Configuring VLAN classifier rules
- Configuring VLAN classifier groups
- Associating a VLAN classifier group to a CEE interface
- Clearing VLAN counter statistics
- Displaying VLAN information
- Configuring the MAC address table
- Configuring STP, RSTP, and MSTP using the CEE CLI
- In this chapter
- STP overview
- RSTP overview
- MSTP overview
- STP, RSTP, and MSTP configuration guidelines and restrictions
- Default STP, RSTP, and MSTP configuration
- STP, RSTP, and MSTP configuration procedures
- STP, RSTP, and MSTP-specific configuration procedures
- STP and RSTP-specific configuration procedures
- RSTP and MSTP-specific configuration procedures
- MSTP-specific configuration procedures
- 10-Gigabit Ethernet CEE interface-specific configuration
- Global STP, RSTP, and MSTP-related configuration procedures
- Clearing STP, RSTP, and MSTP-related information
- Displaying STP, RSTP, and MSTP-related information
- Configuring Link Aggregation using the CEE CLI
- Configuring LLDP using the CEE CLI
- Configuring ACLs using the CEE CLI
- In this chapter
- ACL overview
- Default ACL configuration
- ACL configuration guidelines and restrictions
- ACL configuration procedures
- Creating a standard MAC ACL and adding rules
- Creating an extended MAC ACL and adding rules
- Modifying a MAC ACL
- Removing a MAC ACL
- Reordering the sequence numbers in a MAC ACL
- Applying a MAC ACL to a CEE interface
- Applying a MAC ACL to a VLAN interface
- Clearing MAC ACL counters
- Displaying MAC ACL information
- Configuring QoS using the CEE CLI
- Configuring FCoE using the Fabric OS CLI
- Administering the switch
- Configuring RMON using the CEE CLI
- Index
Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator’s Guide 111
53-1001258-01
Congestion control
8
The basic tail drop algorithm does not have any knowledge of multiple priorities and per traffic
class drop thresholds can be associated with a queue to address this. When the queue depth
breaches a threshold, then any packet arriving with the associated priority value will be dropped.
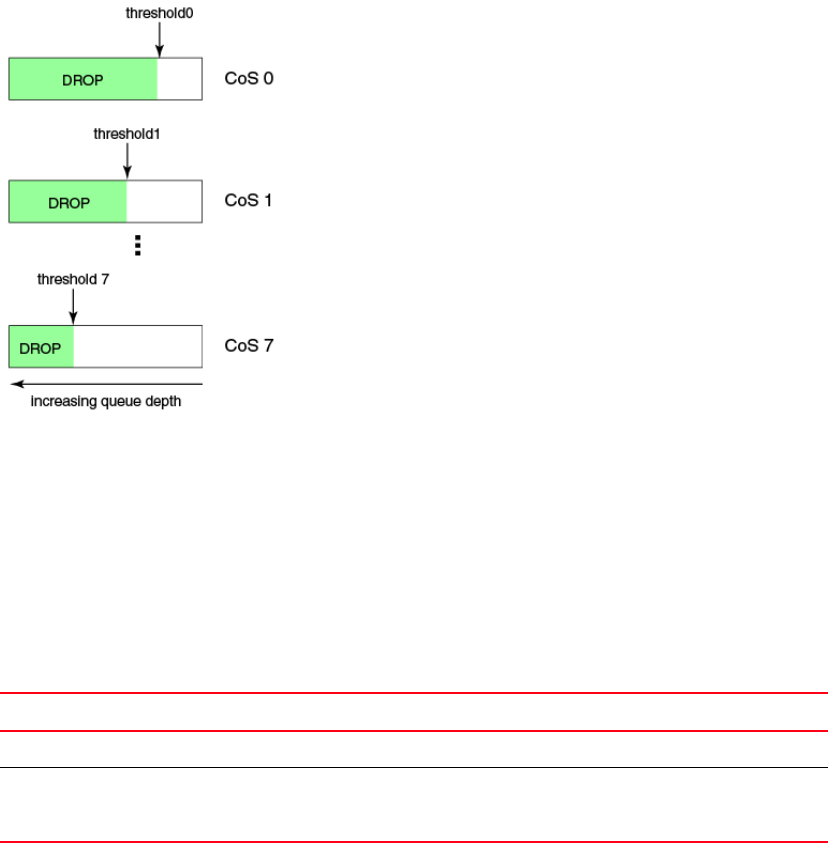
Figure 8 shows how you can utilize this feature to ensure that lower priority traffic cannot totally
consume the full buffer memory. Thresholds can also be used to bound the maximum queueing
delay for each traffic class. Additionally if the sum of the thresholds for a port is set below 100% of
the buffer memory, then you can also ensure that a single port does not monopolize the entire
shared memory pool.
FIGURE 8 Queue depth
The tail drop algorithm can be extended to support per priority drop thresholds. When the ingress
port CoS queue depth breaches a threshold, then any packet arriving with the associated priority
value will be dropped. Figure 8 shows how you can utilize this feature to ensure lower priority traffic
cannot totally consume the full buffer memory. Thresholds can also be used to bound the
maximum queueing delay for each traffic class. Additionally if the sum of the thresholds for a port
is set below 100% of the buffer memory then you can also ensure that a single CoS does not
monopolize the entire shared memory pool allocated to the port.
Changing the Tail Drop threshold
Example of increasing multicast packet expansion Tail Drop Threshold to 1000pkt for each multicast Traffic Class.
switch:admin>cmsh
switch>enable
switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
switch(config)#qos rcv-queue multicast threshold 1000 1000 1000 1000
switch(config)#exit
Step Task Command
1 Enter global configuration mode.
switch#configure terminal
2 Change the Tail Drop threshold for each
multicast traffic class. In this example,
1000pkt is used.
switch(config)#qos rcv-queue
multicast threshold 1000 1000 1000
1000










