HP 3PAR VMware ESX Implementation Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP 3PAR VMware ESX Implementation Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Configuring the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage for Fibre Channel
- 3 Configuring the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage for iSCSI
- 4 Configuring the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage for FCoE
- 5 Configuring the Host for a Fibre Channel Connection
- Installing the HBA and Drivers
- Installing Virtual Machine Guest Operating System
- Multipath Failover Considerations and I/O Load Balancing
- Performance Considerations for Multiple Host Configurations
- ESX/ESXi 4.1, ESXi 5.x Additional Feature Considerations
- Storage I/O Control
- vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI)
- HP 3PAR VAAI Plugin 1.1.1 for ESX 4.1
- HP 3PAR VAAI Plugin 2.2.0 for ESXi 5.x
- UNMAP (Space Reclaim) Storage Hardware Support for ESXi 5.x
- Out-of-Space Condition for ESX 4.1 and ESXi 5.x
- Additional New Primitives Support on ESXi 5.x
- VAAI and New Feature Support Table
- VAAI Plugin Verification
- 6 Configuring the Host as an FCoE Initiator Connecting to a FC target or an FCoE Target
- 7 Configuring the Host for an iSCSI Connection
- Setting Up the Switch, iSCSI Initiator, and iSCSI target ports
- Installing iSCSI on VMware ESX
- Installing Virtual Machine Guest Operating System
- Creating a VMkernel Port
- Configuring a Service Console Connection for the iSCSI Storage
- Configuring the VMware SW iSCSI Initiator
- iSCSI Failover Considerations and Multipath Load Balancing
- Performance Considerations for Multiple Host Configurations
- ESX/ESXi Additional Feature Considerations
- 8 Allocating Storage for Access by the ESX Host
- 9 Booting the VMware ESX Host from the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage
- 10 Support and Other Resources
- 11 Documentation feedback
- A Appendix
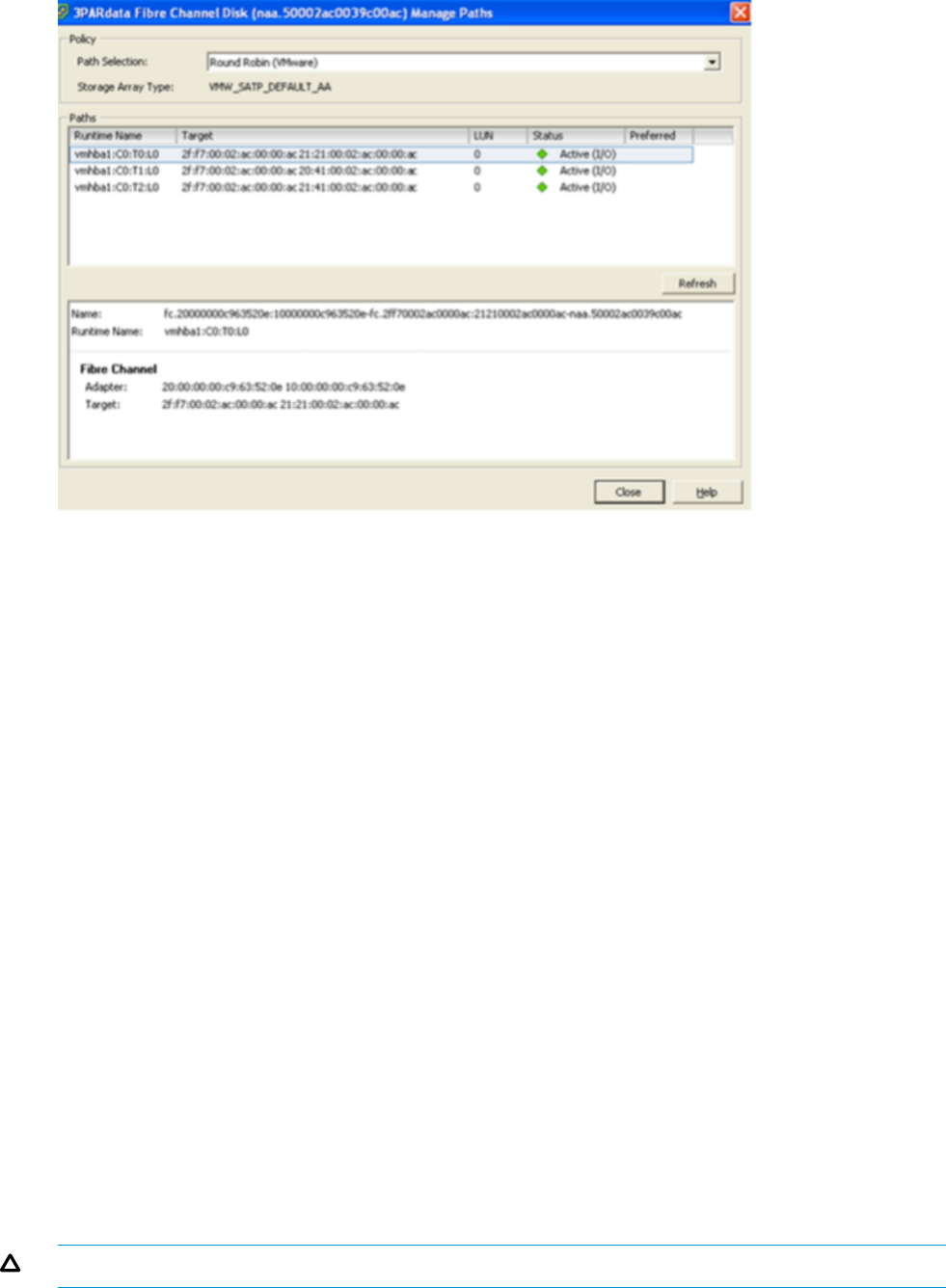
Figure 19 LUN Set to Round Robin
Managing a round robin I/O path policy scheme through the VI/vSphere client GUI for a large
network can be cumbersome and challenging to maintain because the policy must be specified
for each LUN individually and updated whenever new devices are added. Alternatively, VMware
provides a mechanism whereby the server administrator can use esxcli, vCLI, or vSphere
Management Assistant (vMA) commands to manage I/O path policy for storage devices on a
per-host basis using parameters defined within a set of native ESX/ESXi storage plugins.
The VMware native multipathing has two important plugins: a Storage Array Type Plugin (SATP)
that handles path failover and monitors path health, and a path-selection plugin (PSP) that chooses
the best path and routes I/O requests for a specific logical device (PSP defines the path policy).
The correct ESX/ESXi host Storage Array Type Plugin (SATP) to be used is related to the HP 3PAR
array host persona in use. When HP 3PAR host persona 6/Generic-legacy is the host persona
in use with an ESX/ESXi host, the SATP VMW_SATP_DEFAULT_AA should be used. When HP 3PAR
host persona 11/VMware is the host persona in use with an ESX/ESXi host, the SATP
VMW_SATP_ALUA should be used.
For ESX/ESXi 4.0 versions (4.0 GA through all 4.0 updates), the default SATP rules must be edited
in order to automatically achieve a round robin I/O path policy for storage devices.
As of ESX/ESXi 4.1, additional custom SATP rules can be created that target SATP/PSP to specific
vendors while leaving the default SATP rules unmodified. The custom SATP can be used to
automatically achieve a round robin I/O path policy for storage devices.
Configuring ESX/ESXi Multipathing for Round Robin via SATP PSP
As part of PSP Round-Robin configuration, the value of IOPS can be specified. IOPS is the number
of IO operations scheduled for each path during path changes within the Round-Robin path selection
scheme. The default IOPS value is 1000. HP recommends IOPS=100 as an initial value and starting
point for further optimization of IO throughput with PSP Round-Robin. With the exception of ESX/ESXi
4.0 versions, it is preferable to set the IOPS value within a SATP custom rule.
CAUTION: VMware specifically warns not to directly edit the esx.conf file.
Multipath Failover Considerations and I/O Load Balancing 43










