HP 3PAR VMware ESX Implementation Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP 3PAR VMware ESX Implementation Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Configuring the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage for Fibre Channel
- 3 Configuring the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage for iSCSI
- 4 Configuring the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage for FCoE
- 5 Configuring the Host for a Fibre Channel Connection
- Installing the HBA and Drivers
- Installing Virtual Machine Guest Operating System
- Multipath Failover Considerations and I/O Load Balancing
- Performance Considerations for Multiple Host Configurations
- ESX/ESXi 4.1, ESXi 5.x Additional Feature Considerations
- Storage I/O Control
- vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI)
- HP 3PAR VAAI Plugin 1.1.1 for ESX 4.1
- HP 3PAR VAAI Plugin 2.2.0 for ESXi 5.x
- UNMAP (Space Reclaim) Storage Hardware Support for ESXi 5.x
- Out-of-Space Condition for ESX 4.1 and ESXi 5.x
- Additional New Primitives Support on ESXi 5.x
- VAAI and New Feature Support Table
- VAAI Plugin Verification
- 6 Configuring the Host as an FCoE Initiator Connecting to a FC target or an FCoE Target
- 7 Configuring the Host for an iSCSI Connection
- Setting Up the Switch, iSCSI Initiator, and iSCSI target ports
- Installing iSCSI on VMware ESX
- Installing Virtual Machine Guest Operating System
- Creating a VMkernel Port
- Configuring a Service Console Connection for the iSCSI Storage
- Configuring the VMware SW iSCSI Initiator
- iSCSI Failover Considerations and Multipath Load Balancing
- Performance Considerations for Multiple Host Configurations
- ESX/ESXi Additional Feature Considerations
- 8 Allocating Storage for Access by the ESX Host
- 9 Booting the VMware ESX Host from the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage
- 10 Support and Other Resources
- 11 Documentation feedback
- A Appendix

NOTE: VMware and HP recommend the LSI logic adapter emulation for Windows 2003 Servers.
The LSI Logic adapter is also the default option for Windows 2003 when creating a new virtual
machine. HP testing has noted a high incidence of Windows 2003 virtual machine failures during
an ESX multipath failover/failback event when the BUS Logic adapter is used with Windows 2003
VMs.
NOTE: HP testing indicates that the SCSI timeout value for virtual machine guest operating systems
should be 60 seconds in order to successfully ride out path failovers at the ESX layer. Most guest
operating systems supported by VMware have a default SCSI timeout value of 60 seconds, but
this value should be checked and verified for each GOS installation. In particular, Red Hat 4.x
guest operating systems should have their SCSI timeout value changed from their default value of
30 seconds to 60 seconds.
This command line can be used to set the SCSI timeout on all SCSI devices presented to a Red Hat
4.x virtual machine to 60 seconds:
find /sys -name timeout | grep "host.*target.*timeout" | xargs -n 1
echo "echo 60 >"|sh
This must be added as a line in /etc/rc.local of the Red Hat 4.x guest OS in order for the
timeout change to be maintained with a virtual machine reboot.
Example of a modified /etc/rc.local file:
# cat /etc/rc.local
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts.
# You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don't
# want to do the full Sys V style init stuff.
find /sys -name timeout | grep "host.*target.*timeout" | xargs -n 1
echo "echo 60 >"|shtouch /var/lock/subsys/local
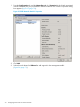
Creating a VMkernel Port
The following steps describe how to set up a VMkernel port. Refer to the VMware vSphere Installation
and Setup guide available at VMware for detailed instructions regarding these settings.
1. Log into the VI/vSphere client and select the server from the inventory panel. The hardware
configuration page for this server appears.
2. Click the Configuration tab and click Networking.
3. Click the Add Networking Link. The Add Network wizard appears (Figure 30 (page 67)).
66 Configuring the Host for an iSCSI Connection