F3215-HP Load Balancing Module Security Configuration Guide-6PW101
14
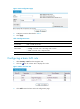
Ste
p
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view. system-view N/A
2. Enter VD system view.
switchto vd vd-name
Required for a security zone of a
non-default VD.
3. Enter security zone
view.
zone name zone-name [ id zone-id ] N/A
4. Enable the share
attribute of the
security zone.
share enable
By default, the share attribute of a
security zone is disabled, and only
the native VD can use the security
zone.
Adding interfaces to a security zone
After you add an interface to a security zone, packets entering or leaving the interface will be matched
against the security policies for the security zone and processed accordingly.
To add an interface to a security zone:
Ste
p
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view N/A
2. Enter VD system view. switchto vd vd-name
Required for a security zone of a
non-default VD.
3. Enter security zone
view.
zone name zone-name [ id zone-id ] N/A
4. Add an interface to
the security zone.
import interface interface-type
interface-number [ vlan vlan-id ]
The default is as follows:
On an LB module, interface
GigabitEthernet 0/1 belongs to
security zone Management and the
other interfaces are not added to
any security zone.
To add a Layer 3 Ethernet interface to a security zone, specify only the interface type and number. You
can perform the import interface command multiple times to add multiple Layer 3 interfaces to a security
zone. Make sure the Layer 3 interfaces to be added and the security zone belong to the same VD. For
more information about assigning an interface to a VD, see System Management Configuration Guide.
To add a Layer 2 Ethernet interface to a security zone, specify both the interface type and number and
the VLANs to which the interface belongs. You can perform the import interface command multiple times
to add the same Layer 2 interface with different native VLANs to the same security zone. Make sure the
VLANs and the security zone belong to the same VD. For more information about assigning a VLAN to
a VD, see System Management Configuration Guide.
Creating an interzone instance
An interzone instance indicates the source zone and destination zone of a data flow to be monitored or
controlled by a security policy, such as a session logging policy. After you apply a security policy to an
interzone instance, the first packet of a data flow traveling from the source zone to the destination zone
will be checked and processed according to the security policy.
The destination zone for an interzone instance must belong to the same VD as the source zone, or have
its share attribute enabled.