F3726, F3211, F3174, R5135, R3816-HP Firewalls and UTM Devices Access Control Configuration Guide-6PW100
4
You can specify a time range in ACL rules before or after you create it. However, the rules using the time
range take effect only after you define the time range.
104BFragments filtering with ACLs
Traditional packet filtering matches only first fragments of packets, and allows all subsequent non-first
fragments to pass through. Attackers can fabricate non-first fragments to attack networks.
To avoid the risks, the HP ACL implementation does the following:
• Filters all fragments by default, including non-first fragments.
• Allows for matching criteria modification, for example, filters non-first fragments only.
20B
Configuring the ACL in the Web interface
105BRecommended IPv4 basic ACL configuration procedure
IPv4 basic ACLs match packets based only on source IP addresses.
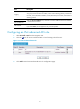
Complete the following tasks to configure an IPv4 basic ACL:
Task Remarks
1. Create an IPv4 basic ACL.
Required.
For more information, see "
545H
Creating an ACL".
2. 546HConfiguring an IPv4 basic ACL rule.
Required.
106BRecommended IPv4 advanced ACL configuration procedure
IPv4 advanced ACLs match packets based on source IP addresses, destination IP addresses, packet
priorities, protocols over IP, and other protocol header information, such as TCP/UDP source and
destination port numbers, TCP flags, ICMP message types, and ICMP message codes.
Compared to IPv4 basic ACLs, IPv4 advanced ACLs allow more flexible and accurate filtering.
Complete the following tasks to configure an IPv4 advanced ACL:
Task Remarks
1. Create an IPv4 advanced ACL.
Required.
For more information, see "
547H
Creating an ACL".
2. 548HConfiguring an IPv4 advanced ACL rule. Required.
107BRecommended Ethernet frame header ACL configuration
procedure
Ethernet frame header ACLs, also called "Layer 2 ACLs," match packets based on Layer 2 protocol
header fields, such as source MAC address, destination MAC address, 802.1p priority (VLAN priority),
and link layer protocol type.