F3726, F3211, F3174, R5135, R3816-HP Firewalls and UTM Devices Access Control Configuration Guide-6PW100
40
source zone to the destination zone will be checked and processed according to the security policy. For
more information about ASPF policies, interzone policies, and session logging, see Attack Protection
Configuration Guide and Access Control Configuration Guide.
The destination zone for an interzone instance must belong to the same VD as the source zone, or have
its share attribute enabled. To specify a security zone that belongs to a different VD than the source zone
as the destination zone, enter the zone name in the format vd-name-zone-id. For example, to specify VD
test's zone 2 as the destination zone, enter test-2.
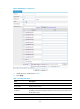
To create an interzone instance:
Ste
p
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view. system-view N/A
2. Enter VD system view.
switchto vd vd-name Required for a security zone of a non-default VD.
3. Create an interzone
instance and enter
interzone instance
view.
interzone source
source-zone-name
destination
destination-zone-name
By default, no interzone instance exists.
26B
Security zone configuration example
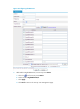
277BNetwork requirements
As shown in 580HFigure 31, a company deploys a firewall to connect its internal network to the Internet, and
needs to provide WWW service and FTP service for external users.
Configure the firewall so that:
• Internal users can access the WWW and FTP servers and the Internet.
• External users can only access the servers.
Figure 31 Network diagram
278BConfiguration considerations
Three security zones are needed: one for the internal users, one for the servers, and one for the external
users, in the order of priority (from high to low). The default zones Trust, DMZ, and Untrust can answer
the requirements for security zones.