F3726, F3211, F3174, R5135, R3816-HP Firewalls and UTM Devices NAT and ALG Configuration Guide-6PW100
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Configuring NAT
- Overview
- Configuration guidelines
- Configuring NAT in the Web interface
- Recommended configuration procedure
- Creating an address pool
- Configuring dynamic NAT on an interface
- Creating a static address mapping
- Enabling static NAT on an interface
- Configuring an internal server
- Configuring ACL-based NAT on the internal server
- Configuring DNS mapping
- NAT configuration example
- Internal server configuration example
- Configuring NAT at the CLI
- NAT configuration task list
- Configuring static NAT
- Configuring dynamic NAT
- Configuring an internal server
- Configuring ACL-based NAT on an internal server
- Configuring DNS mapping
- Displaying and maintaining NAT
- One-to-one static NAT configuration example
- Dynamic NAT configuration example
- Common internal server configuration example
- NAT DNS mapping configuration example
- Troubleshooting NAT
- Configuring NAT-PT
- Feature and hardware compatibility
- Overview
- NAT-PT configuration task list
- Configuration prerequisites
- Enabling NAT-PT
- Configuring a NAT-PT prefix
- Configuring IPv4/IPv6 address mappings on the IPv6 side
- Configuring IPv4/IPv6 address mappings on the IPv4 side
- Setting the ToS field after NAT-PT translation
- Setting the traffic class field after NAT-PT translation
- Configuring static NAPT-PT mappings of IPv6 servers
- Displaying and maintaining NAT-PT
- NAT-PT configuration examples
- Troubleshooting NAT-PT
- NAT444
- Configuring ALG
- Support and other resources
- Index
34
2BConfiguring NAT-PT
NAT-PT can be configured only at the CLI.
NAT-PT is not supported on VLAN interfaces and does not support VPN instances, IPv4 fragments, or
ICMPv6 fragments.
11B
Feature and hardware compatibility
Hardware NAT-PT com
p
atible
F1000-A-EI/F1000-S-EI Yes
F1000-E Yes
F5000 Yes
Firewall module Yes
U200-A Yes
U200-S No
12B
Overview
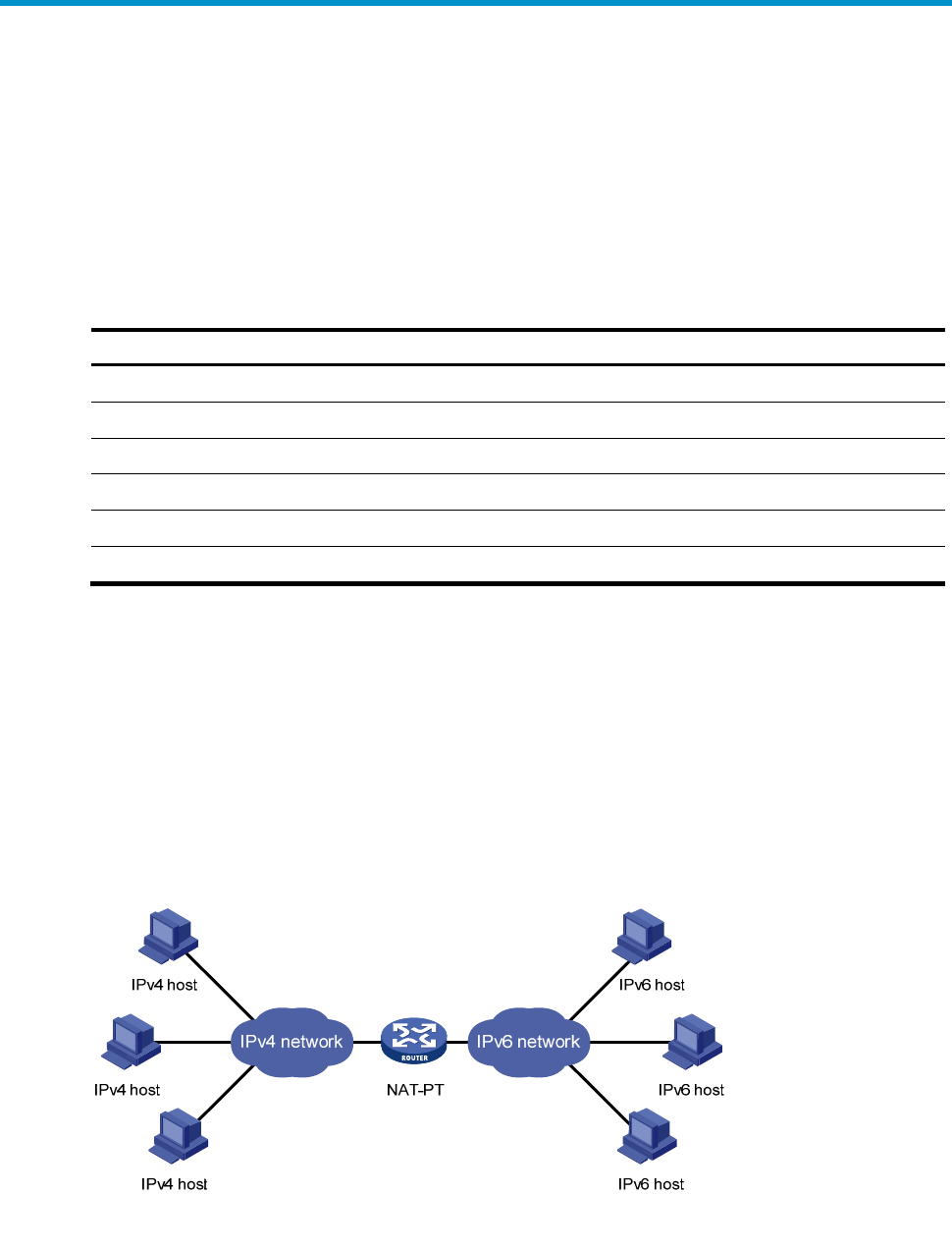
Because of the coexistence of IPv4 networks and IPv6 networks, Network Address Translation–Protocol
Translation (NAT-PT) was introduced to realize translation between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. For
example, it can enable a host in an IPv6 network to access the FTP server in an IPv4 network.
As shown in
260HFigure 30, NAT-PT runs on the device between IPv4 and IPv6 networks. The address
translation is transparent to both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. Users in the IPv6 and IPv4 networks can
communicate without changing their configurations.
Figure 30 Network diagram










