F3726, F3211, F3174, R5135, R3816-HP Firewalls and UTM Devices NAT and ALG Configuration Guide-6PW100
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Configuring NAT
- Overview
- Configuration guidelines
- Configuring NAT in the Web interface
- Recommended configuration procedure
- Creating an address pool
- Configuring dynamic NAT on an interface
- Creating a static address mapping
- Enabling static NAT on an interface
- Configuring an internal server
- Configuring ACL-based NAT on the internal server
- Configuring DNS mapping
- NAT configuration example
- Internal server configuration example
- Configuring NAT at the CLI
- NAT configuration task list
- Configuring static NAT
- Configuring dynamic NAT
- Configuring an internal server
- Configuring ACL-based NAT on an internal server
- Configuring DNS mapping
- Displaying and maintaining NAT
- One-to-one static NAT configuration example
- Dynamic NAT configuration example
- Common internal server configuration example
- NAT DNS mapping configuration example
- Troubleshooting NAT
- Configuring NAT-PT
- Feature and hardware compatibility
- Overview
- NAT-PT configuration task list
- Configuration prerequisites
- Enabling NAT-PT
- Configuring a NAT-PT prefix
- Configuring IPv4/IPv6 address mappings on the IPv6 side
- Configuring IPv4/IPv6 address mappings on the IPv4 side
- Setting the ToS field after NAT-PT translation
- Setting the traffic class field after NAT-PT translation
- Configuring static NAPT-PT mappings of IPv6 servers
- Displaying and maintaining NAT-PT
- NAT-PT configuration examples
- Troubleshooting NAT-PT
- NAT444
- Configuring ALG
- Support and other resources
- Index
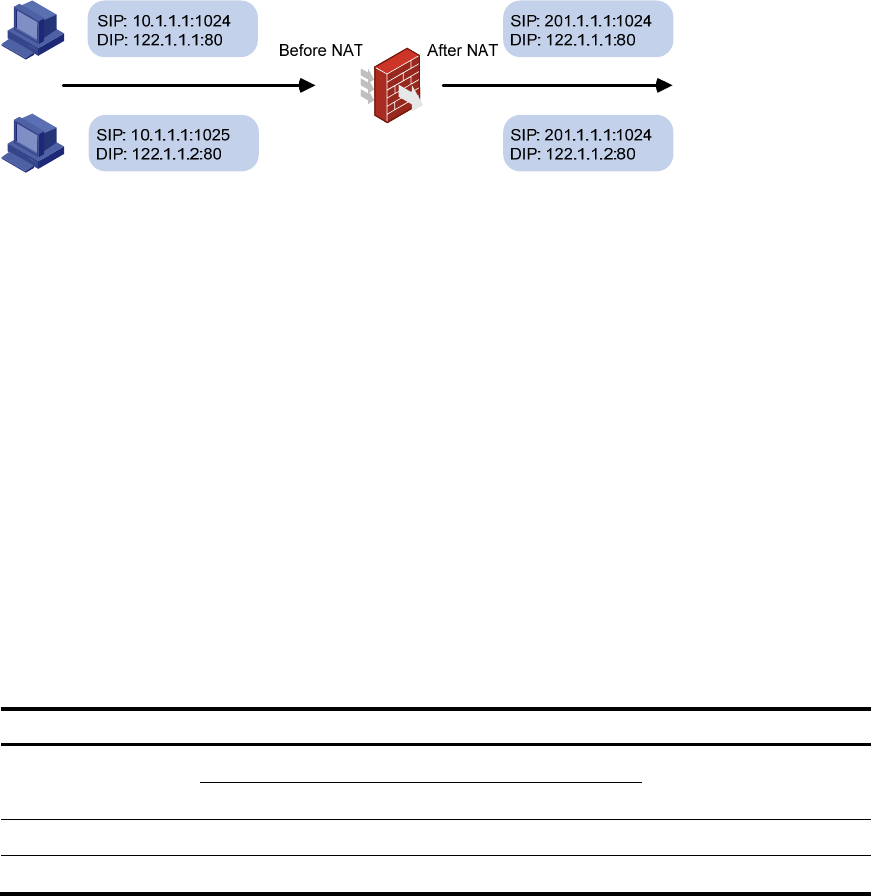
48
Figure 36 NAT unlimited connection
85BUser connection limit
You can use connection limit to prevent large amount of resources being occupied because of excessive
sessions and to prevent external attacks after FullCone NAT is enabled.
86BFull cone NAT
Enable Full cone NAT when the P2P node is behind a NAT device and provides external download
services.
87BMultiple routing protocols
NAT444 supports static routes and policy-based routes as well as dynamic routes such as OSPF, BGP,
and ISIS.
28B
NAT444 configuration task list
Task Remarks
Configuring NAT444
276H
Configuring NAT444 static IP-port mappings
Either is required.
277H
Configuring NAT444 dynamic IP-port mappings
278H
Configuring Full cone NAT Optional.
279H
Configuring NAT444 logging Optional.
When static NAT444, dynamic NAT444, static NAT, and dynamic NAT all exist and are used for
matching the same flows, the matching sequence is as follows:
1. Static NAT.
2. Static NAT444.
3. For dynamic NAT444 and dynamic NAT, ACLs are matched in descending order.
29B
Configuring NAT444 static IP-port mappings
By configuring an internal-to-external IP-port mapping manually, NAT444 assigns a public address and
a port block to each user of the private address pool. CGN uses the specified public address and port
block to translate the private source IP and port when an internal user accesses an external network.
To configure a NAT444 static IP-port mapping in system view:










