HP VPN Firewall Appliances Network Management Configuration Guide
279
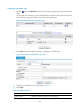
2. The QoS module takes various QoS actions on classified traffic as configured, depending on the
traffic processing phase and network status. For example, you can configure the QoS module to
perform traffic policing for incoming traffic, traffic shaping for outgoing traffic, congestion
avoidance before congestion occurs, and congestion management when congestion occurs.
Figure 179 QoS processing flow
QoS configuration approaches
QoS configuration approach overview
You can configure QoS by using the following approaches:
• MQC approach
• Non-MQC approach
S
ome features support both appr
oaches, but some support only one.
MQC approach
In the modular QoS configuration (MQC) approach, you configure QoS service parameters by using
QoS policies. A QoS policy defines the shaping, policing, or other QoS actions to take on different
classes of traffic. It is a set of class-behavior associations.
A class is a set of match criteria for identifying traffic, and it uses the AND or OR operator:
• If the operator is AND, a packet must match all the criteria to match the class.
• If the operator is OR, a packet matches the class if it matches any of the criteria in the class.
A traffic behavior defines a set of QoS actions to take on packets, such as priority marking and redirect.
By associating a traffic behavior with a class in a QoS policy, you apply the specific set of QoS actions
to the class of traffic.
Traffic policing
Priority marking
Classify the
traffic
Classification
Packets received
on the interface
Tokens
Drop
Other
proce
ssing
Token bucket
CAR Remark
Toekn
Classify the
traffic
Classification
Packets to be
sent out the
interface
Drop
Other
proces
sing
Drop
Queuing
Enqueue
Queue 0
Queue 1
Queue 2
Queue N
Dequeue
Transmit
Queues
Token bucket
Traffic policing
Traffic shaping
Congestion
avoidance
CAR
GTS
WRED
Congestion
management