R3166-R3206-HP High-End Firewalls VPN Configuration Guide-6PW101
90
L2TP configuration
L2TP overview
The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is one of the most commonly used Virtual Private Dial-up Network
(VPDN) tunneling protocol.
Typical networking application of L2TP
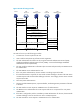
Figure 54 shows a typical VPDN built by using L2TP.
Figure 54 VPDN built by using L2TP
A VPDN built by using L2TP consists of the following components:
• Remote system
A remote system is usually a remote user’s host or a remote branch’s routing device that needs to access
the VPDN network.
• LAC
An L2TP access concentrator (LAC) is a device that has PPP and L2TP capabilities. An LAC is usually a
Network Access Server (NAS) located at a local ISP, which provides access services mainly for PPP users.
An LAC is an endpoint of an L2TP tunnel and lies between an LNS and a remote system. It encapsulates
packets received from a remote system using L2TP and then sends the resulting packets to the LNS. It
de-encapsulates packets received from the LNS and then sends the resulting packets to the intended
remote system.
Usually, a PPP link is used in a VPDN application.
• LNS
An L2TP network server (LNS) functions as both the L2TP server and the PPP end system. It is usually an
edge device on an enterprise network.
An LNS is the other endpoint of an L2TP tunnel and is a peer to the LAC. It is the logical termination point
of a PPP session tunneled by the LAC. The L2TP extends the termination point of a PPP session from a NAS
to an LNS, logically.