R3204P16-HP Load Balancing Module Network Management Configuration Guide-6PW101
Table Of Contents
- Title page
- Contents
- Interface management configuration
- IP addressing configuration
- MAC address table configuration
- Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- Layer 2 forwarding overview
- Configuring general Layer 2 forwarding
- Configuring inline Layer 2 forwarding
- Configuring inter-VLAN Layer 2 forwarding
- Forward-type inline Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- Blackhole-type inline Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- Inter-VLAN Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- VLAN configuration
- ARP configuration
- Gratuitous ARP configuration
- Proxy ARP configuration
- Layer 3 forwarding configuration
- NAT configuration
- Overview
- Configuring a NAT policy in the web interface
- Configuring NAT in the CLIs
- Configuration guidelines
- ALG configuration
- Static route configuration
- RIP configuration
- OSPF configuration
- BGP configuration
- Policy-based routing configuration
- Route displaying
- DNS configuration
- Overview
- Configuring DNS on the web interface
- Configuring DNS in the CLIs
- Troubleshooting IPv4 DNS configuration
- Support and other resources
- Index
116
NOTE:
• When confi
g
urin
g
a static route, the static route does not take effect if you specify the next hop address
first and then configure it as the IP address of a local interface, such as Ethernet interface and VLAN
interface.
• If you do not specify the preference when confi
g
urin
g
a static route, the default preference will be used.
Reconfiguring the default preference applies only to newly created static routes.
• You can flexibly control static routes by configuring tag values and using the tag values in the routing
policy.
• If the destination IP address and mask are both configured as 0.0.0.0 with the ip route-static command,
the route is the default route.
Displaying and maintaining static routes
To do… Use the command…
Remarks
Display information of
static routes
display ip routing-table protocol static [ inactive | verbose ]
Available in any
view
Delete all the static
routes
delete static-routes all
Available in
system view
Static route configuration example
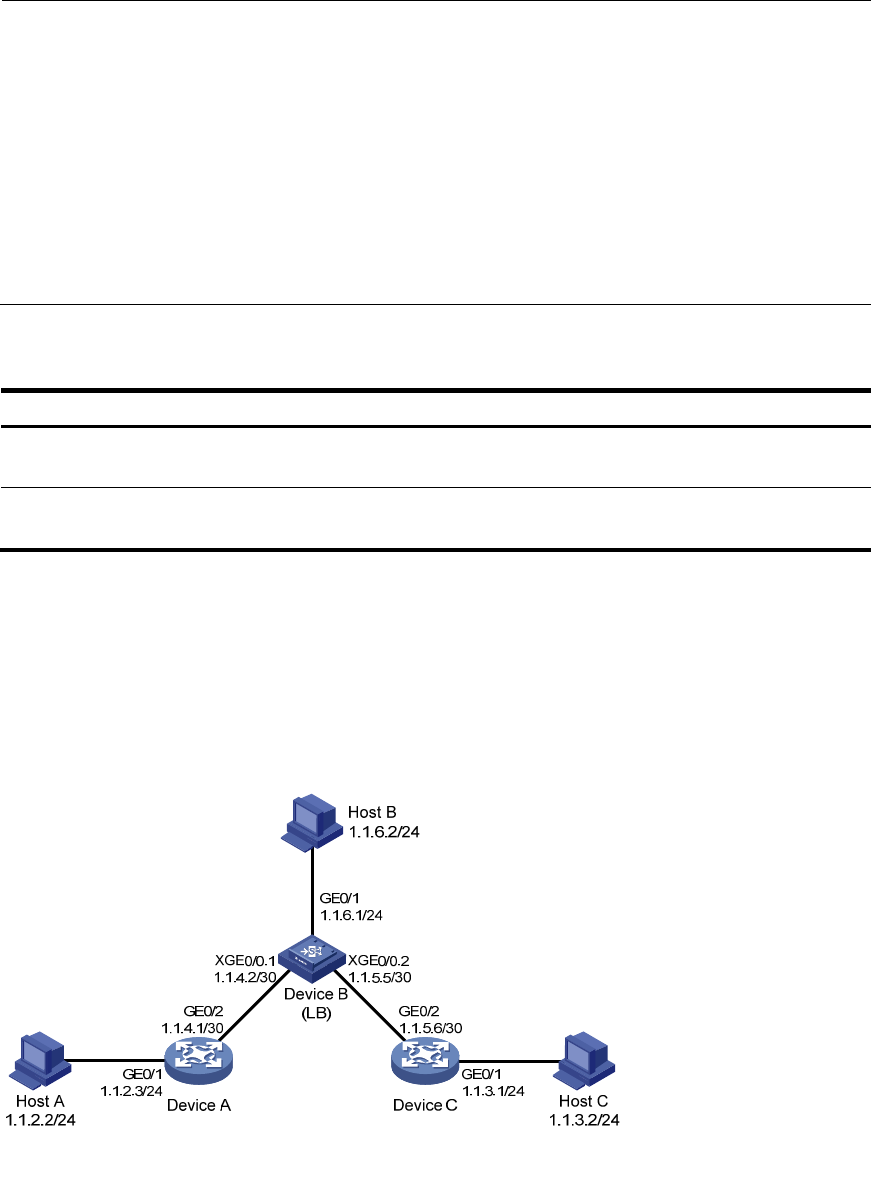
Network requirements
The IP addresses and masks of routers’ interfaces, LB module’s interfaces, and the hosts are shown
in Figure 73. C
onfigure static routes for interconnections between any two hosts.
Figure 73 Network diagram for static route configuration
Configuration procedure
1. Configuring IP addresses for interfaces (omitted)
2. Configuring static routes
# Configure a default route on Device A.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.4.2










