R3204P16-HP Load Balancing Module Network Management Configuration Guide-6PW101
Table Of Contents
- Title page
- Contents
- Interface management configuration
- IP addressing configuration
- MAC address table configuration
- Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- Layer 2 forwarding overview
- Configuring general Layer 2 forwarding
- Configuring inline Layer 2 forwarding
- Configuring inter-VLAN Layer 2 forwarding
- Forward-type inline Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- Blackhole-type inline Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- Inter-VLAN Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- VLAN configuration
- ARP configuration
- Gratuitous ARP configuration
- Proxy ARP configuration
- Layer 3 forwarding configuration
- NAT configuration
- Overview
- Configuring a NAT policy in the web interface
- Configuring NAT in the CLIs
- Configuration guidelines
- ALG configuration
- Static route configuration
- RIP configuration
- OSPF configuration
- BGP configuration
- Policy-based routing configuration
- Route displaying
- DNS configuration
- Overview
- Configuring DNS on the web interface
- Configuring DNS in the CLIs
- Troubleshooting IPv4 DNS configuration
- Support and other resources
- Index
16
IP addressing configuration
NOTE:
You can configure IP addresses in the web interface or at the CLI. For more information about the web
configuration procedure, see the chapter “Interface management configuration.” This chapter introduces
how to configure IP addresses at the CLI only.
IP addressing overview
IP address classes
IP addressing uses a 32-bit address to identify each host on a network. To make IP addresses easier to
read, they are written in dotted decimal notation, each address being four octets in length. For example,
address 00001000000000010000000100000001 in binary is written as 10.1.1.1.
Each IP address breaks down into two parts:
• Net ID: Identifies a network. The first several bits of a net ID, known as the class field or class bits,
identify the class of an IP address.
• Host ID: Identifies a host on a network.
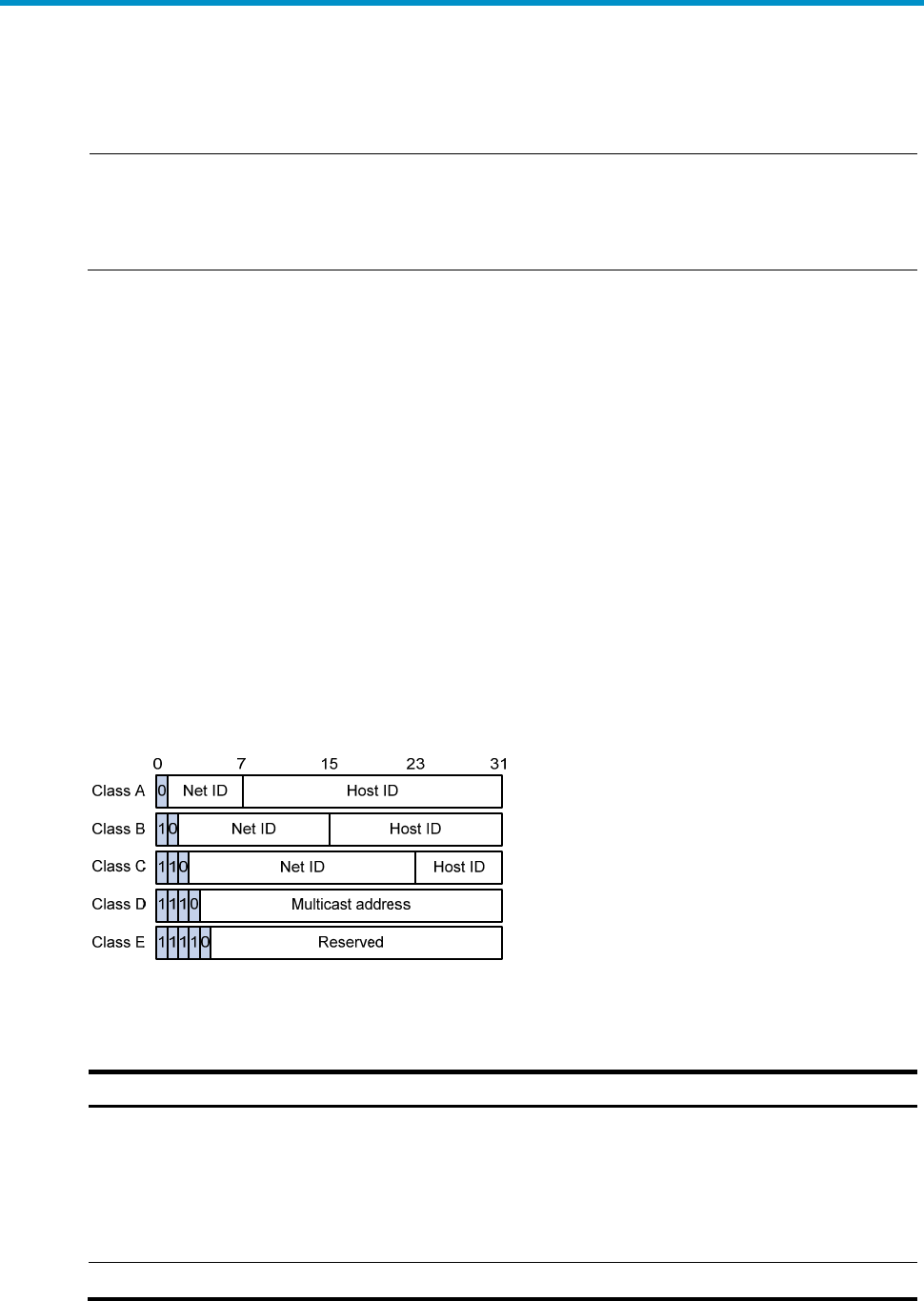
IP addresses are divided into five classes, as shown in Figure 5. T
he shaded areas represent the address
class. The first three classes are widely used.
Figure 5 IP address classes
Table 3 describes the address ranges of these five classes.
Table 3 IP address classes and ranges
Class Address ran
g
e Remarks
A 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255
The IP address 0.0.0.0 is used by a host at bootstrap for
temporary communication. This address is never a valid
destination address.
Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback
test. Packets destined to these addresses are processed
locally as input packets rather than sent to the link.
B 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 ––










