R3204P16-HP Load Balancing Module Network Management Configuration Guide-6PW101
Table Of Contents
- Title page
- Contents
- Interface management configuration
- IP addressing configuration
- MAC address table configuration
- Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- Layer 2 forwarding overview
- Configuring general Layer 2 forwarding
- Configuring inline Layer 2 forwarding
- Configuring inter-VLAN Layer 2 forwarding
- Forward-type inline Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- Blackhole-type inline Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- Inter-VLAN Layer 2 forwarding configuration example
- VLAN configuration
- ARP configuration
- Gratuitous ARP configuration
- Proxy ARP configuration
- Layer 3 forwarding configuration
- NAT configuration
- Overview
- Configuring a NAT policy in the web interface
- Configuring NAT in the CLIs
- Configuration guidelines
- ALG configuration
- Static route configuration
- RIP configuration
- OSPF configuration
- BGP configuration
- Policy-based routing configuration
- Route displaying
- DNS configuration
- Overview
- Configuring DNS on the web interface
- Configuring DNS in the CLIs
- Troubleshooting IPv4 DNS configuration
- Support and other resources
- Index
65
Proxy ARP configuration
NOTE:
The LB module supports proxy ARP configuration only in the CLIs.
This chapter includes these sections:
Proxy ARP overview
If a host sends an ARP request for the MAC address of another host that actually resides on another
network (but the sending host considers the requested host is on the same network) or that is isolated from
the sending host at Layer 2, the device in between must be able to respond to the request with the MAC
address of the receiving interface to allow Layer 3 communication between the two hosts. This is
achieved by proxy ARP. Proxy ARP hides the physical details of the network.
Proxy ARP involves common proxy ARP and local proxy ARP, which are described in the following
sections.
NOTE:
The term proxy ARP in the followin
g
sections of this chapter refers to common proxy ARP unless otherwise
specified.
Proxy ARP
A proxy ARP enabled LB card allows hosts that reside on different subnets to communicate.
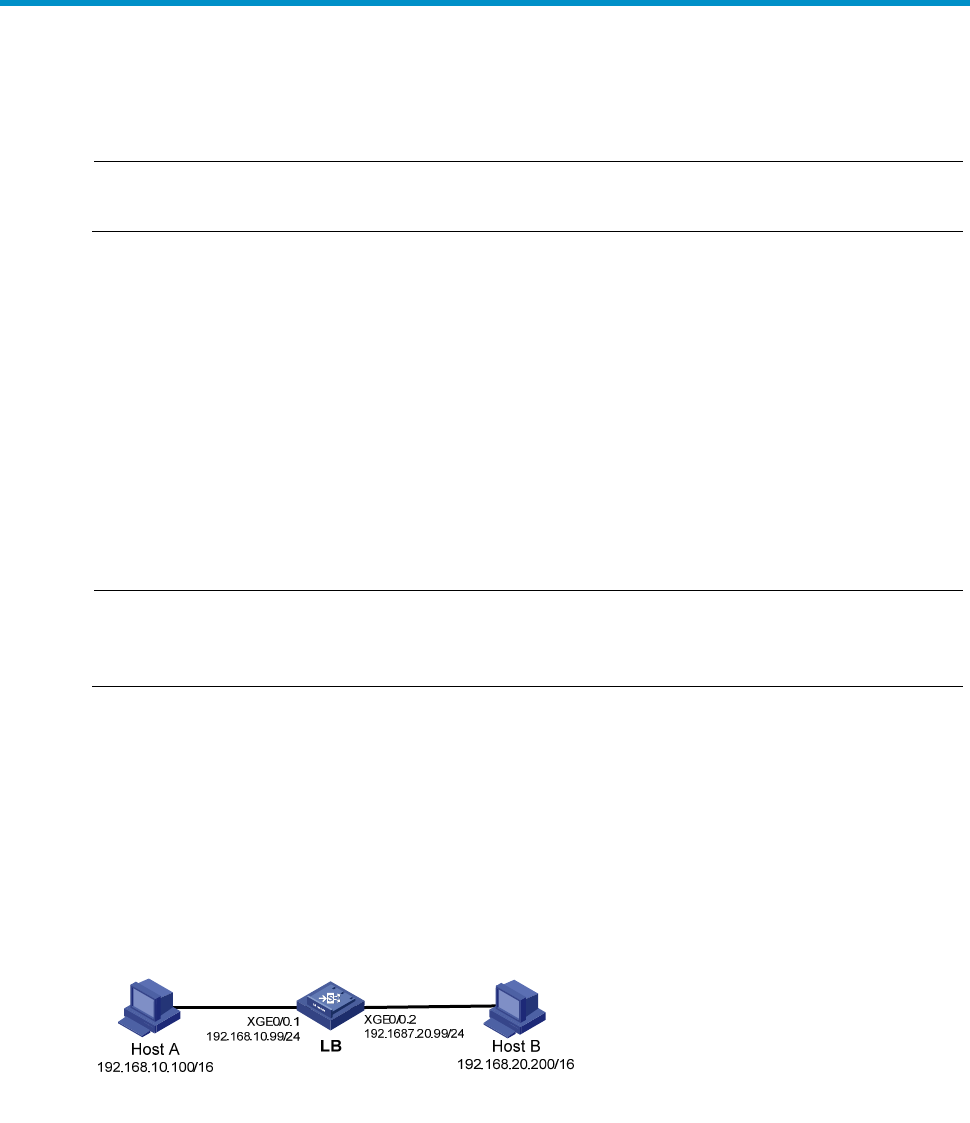
As shown in Figure 32,
LB module connects to two subnets through Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0.1 and
Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0.2. The IP addresses of the two interfaces are 192.168.10.99/24 and
192.168.20.99/24. Host A and Host B have the same prefix 192.168.0.0 assigned and connect to
Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0.1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0.2, respectively.
Figure 32 Application environment of proxy ARP
Because Host A considers that Host B is on the same network, it directly sends an ARP request for the
MAC address of Host B. Host B, however, cannot receive this request because it locates in a different
broadcast domain.
You can solve the problem by enabling proxy ARP on LB module. After that, LB module can reply to the
ARP request from Host A with the MAC address of Ethernet 1/1, and forward packets sent from Host A
to Host B. LB module acts as a proxy of Host B.










