HP Data Protector Software Cell Manager Planning and Sizing
Table Of Contents
- Executive summary
- Solution description
- Cell Manager software topology
- IDB architecture
- Why should you configure the IDB?
- Regular IDB backups
- IDB notifications
- Limitations
- IDB Growth and Performance
- IDB key growth factors
- IDB key performance factors
- IDB key growth and performance parameters
- Influence of logging level on IDB
- Example: Changing of logging level for filesystem backup
- Influence of catalog protection on IDB
- Example: Changing of catalog protection of a backup
- Recommended usage of logging level and catalog protection
- Use different logging levels in the same cell
- Different logging levels for ObjectCopies
- Specifics for small cells
- Specifics for large cells
- Maintenance of DCBF directories
- Cell Manager hardware aspects to consider
- Cluster support for Data Protector software Cell Manager
- Security
- IDB space consumption example
- Cell Manager requirements
- For more information
Catalog Database (CDB)
CDB records
The Catalog Database stores information about the following:
• Backup, restore, copy, object consolidation, and media management sessions
This is the copy of the information sent to the Data Protector Monitor window.
• Backed up objects, their versions, and object copies
• Positions of backed up objects on media
For each backed up object, Data Protector stores information about the media and data segments
used for the backup. The same is done for object copies and object mirrors.
• Pathnames of backed up files (filenames) together with client system names
Filenames are stored only once per client system. The filenames created between backups are
added to the CDB.
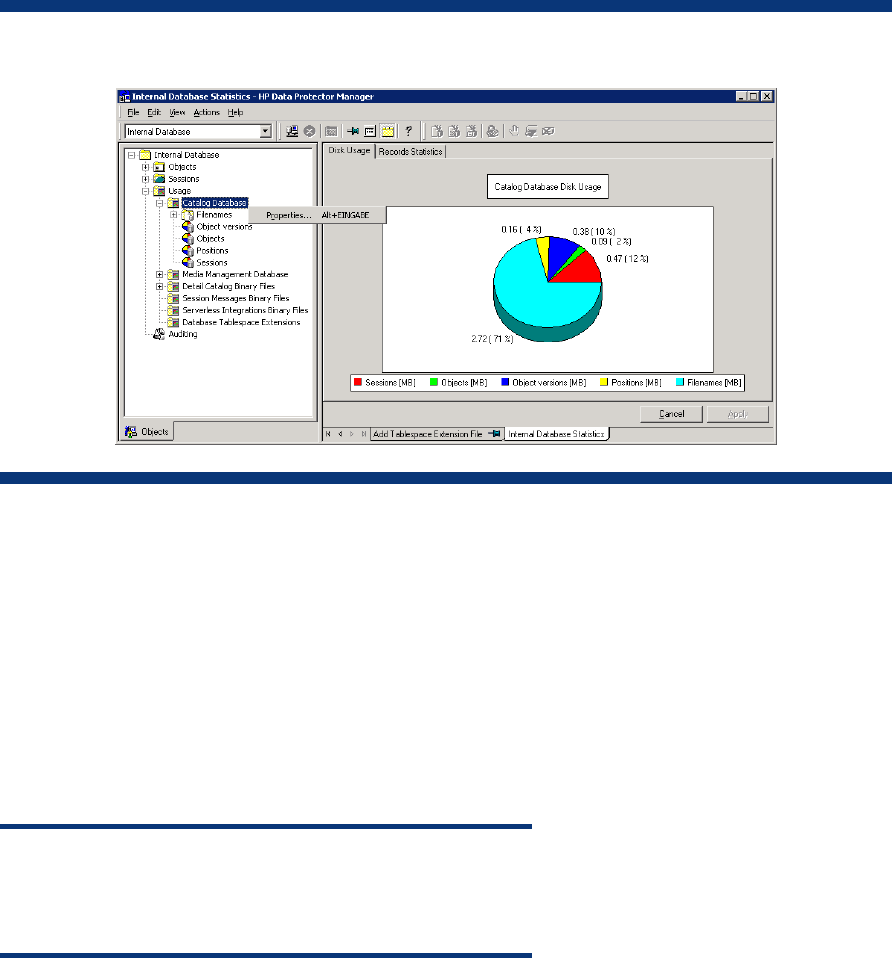
Figure 3 depicts the properties of the catalog database of an existing IDB.
Figure 3: IDB catalog database properties
CDB (filenames) size and growth
The biggest and fastest growing part of the CDB is the filenames part. It typically occupies 20% of the
entire database.
The growth of the filenames part is proportional to the growth and dynamics of the backup
environment and not to the number of backups.
A file or directory in the IDB occupies approximately 50–70 bytes on the UNIX Cell Manager and
70–100 bytes on the Windows Cell Manager.
Filenames are stored in the fnames.dat file and in some other files, depending on the filename length.
The maximum size of each of these data files is 2 GB. You are notified when one of these files starts
running out of space, so that you can add new files to extend the size of the filenames part of the IDB.
Note:
The filenames of object copies are not added to the IDB. Object copying
does not produce any impact on the filename part of the CDB if its logging
level is the same or less detailed than the logging level of its source object.
8










