R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 FCoE Configuration Guide
2
NOTE:
• An FC SAN refers to a network comprising FCF switches and nodes.
• A fabric refers to a transmission network comprising FCF switches.
FC protocol
The servers, FCF switches, and disk devices in an FC SAN must all support FC.
Basic concepts
WWN
The World Wide Name (WWN) is a 64-bit address that identifies a fabric or an entity (such as an FCF
switch, node, or port) in an FC SAN. The upper-layer protocol of FC uses WWNs for communication.
Each entity has a factory-assigned globally unique WWN.
FC address
The FC protocol accesses communication entities in a SAN through FC addresses. An FC address is also
known as an "FC_ID."
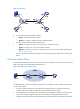
Figure 2 sho
ws the structure of an FC address. The FC address is 24 bits long and is divided into these
8-bit fields: Domain_ID, Area_ID, and Port_ID.
• A domain represents a switch and all N_Ports connected to the switch. A Domain_ID, which is in the
range of 1 to 239, uniquely identifies an FCF switch.
• One or more N_Ports on the same node can be assigned to an area, which is identified by an
Area_ID.
• The Port_ID field identifies an N_Port.
Figure 2 Structure of an FC address
A Domain_ID can uniquely identify an FCF switch. Different FCF switches in the same fabric have
different Domain_IDs.
An FC address can uniquely identify an N_Port on a node. Different N_Ports on the same node have
different FC addresses. FCF switches use Domain_IDs to route messages between each other.
The FC protocol standardizes the FC address usage. For more information, see "Appendixes."
Interface modes
In a switched fabric, nodes and FCF switches communicate through interfaces of different modes.