R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 High Availability Configuration Guide
41
• Routers in a VRRP group determine their roles by priority. The router with the highest priority is
elected as the master, and the others are the backups. The master periodically sends VRRP
advertisements to notify the backups that it is operating correctly, and each of the backups starts a
timer to wait for advertisements from the master.
• In preemptive mode, when a backup receives a VRRP advertisement, it compares only the priority
in the packet with its own priority. If the priority of the backup is higher, the backup becomes the
master and periodically sends VRRP advertisements. Otherwise, it remains as backup. In
preemptive mode, the router with the highest priority in a VRRP group always acts as the master for
packet forwarding.
• In non-preemptive mode, a router in the VRRP group remains a master or backup as long as the
master does not fail. A backup does not become the master even if it is configured with a higher
priority.
• If a backup does not receive any VRRP advertisement when the timer (3 × advertisement interval +
Skew_Time) expires, it considers that the master fails, and takes over as the master and sends VRRP
advertisements.
• When multiple routers in a VRRP group declare that they are the master because of network
problems, the one with the highest priority becomes the master. If two routers have the same priority,
the one with the highest IP address becomes the master.
VRRP tracking
To enable VRRP tracking, configure the routers in the VRRP group to operate in preemptive mode first, so
that only the router with the highest priority operates as the master for packet forwarding. For more
information about track entries, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
The VRRP tracking function uses network quality analyzer (NQA) or bidirectional forwarding detection
(BFD) to monitor the state of the master, and establishes the collaboration between the VRRP device state
and NQA or BFD through the Track function. It implements the following:
• Monitors the upstream link and changes the priority of the router according to the state of the link.
If the upstream link fails, the hosts on the subnet cannot access external networks through the router
and the state of the track entry becomes Negative. The priority of the master decreases by a
specified value. Then, a router with a higher priority in the VRRP group becomes the master to
maintain the proper communication between the hosts on the subnet and external networks.
• Monitors the state of the master on the backups. When the master fails, a backup immediately takes
over as the master to ensure uninterrupted communication.
When the track entry changes from Negative to Positive or Notready, the router automatically restores its
priority. For more information about track entries, see "Configuring Track."
VRRP application
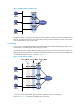
Master/backup
In master/backup mode, only the master forwards packets, as shown in Figure 14. When the master fails,
a new master is elected from among the backups. This mode requires only one VRRP group, and each
router in the group has a different priority. The one with the highest priority becomes the master.