R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MLD snooping
- Overview
- MLD snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions
- Configuring MLD snooping port functions
- Configuring MLD snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining MLD snooping
- MLD snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD snooping
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- PIM overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Support and other resources
- Index
156
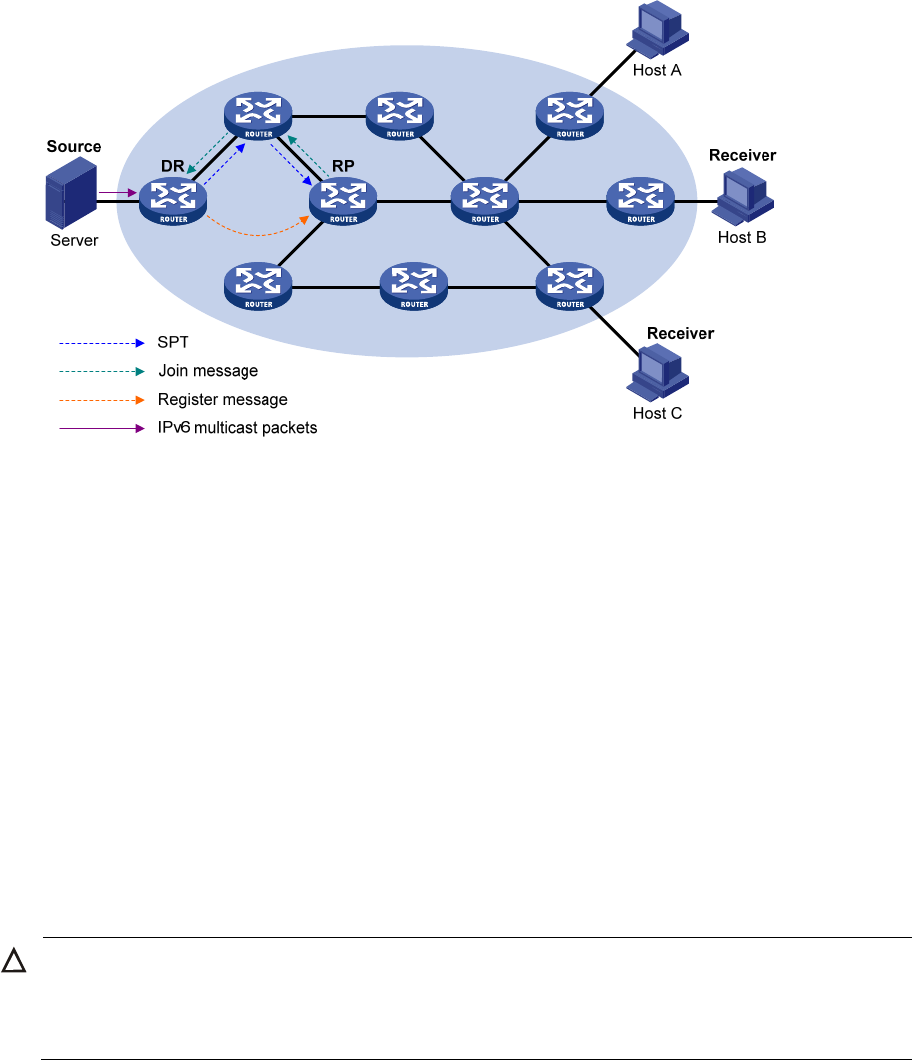
Figure 50 IPv6 multicast source registration
As shown in Figure 50, the IPv6 multicast source registers with the RP as follows:
1. The IPv6 multicast source S sends the first multicast packet to the IPv6 multicast group G. When
receiving the multicast packet, the source-side DR that directly connects to the IPv6 multicast source
encapsulates the packet in an register message and unicasts the message to the RP.
2. After the RP receives the register message, it decapsulates it and forwards it down to the RPT.
Meanwhile, it sends an (S, G) source-specific join message hop by hop toward the IPv6 multicast
source. The routers along the path from the RP to the IPv6 multicast source constitute an SPT branch,
and each router on this branch creates an (S, G) entry in its forwarding table. The SPT is rooted at
the source-side DR, and has the RP as its leaf.
3. The subsequent IPv6 multicast data from the IPv6 multicast source are forwarded to the RP along
the established branch, and the RP forwards the data to the receivers along the RPT. When the IPv6
multicast data reaches the RP along the SPT, the RP unicasts a register-stop message to the
source-side DR to prevent the DR from unnecessarily encapsulating the data.
CAUTION:
If the switch is an RP, disablin
g
switchover to SPT mi
g
ht cause multicast traffic forwardin
g
failures on the
source-side DR. When disabling switchover to SPT, be sure you fully understand its impact on your
network.
Switchover to SPT
In an IPv6 PIM-SM domain, only one RP and one RPT provide services for a specific IPv6 multicast group.
Before the switchover to SPT occurs, the source-side DR encapsulates all IPv6 multicast data addressed to
the IPv6 multicast group in register messages and sends them to the RP. After receiving these register
messages, the RP decapsulates them and forwards them to the receivers-side DR along the RPT.
Switchover to SPT has the following weaknesses:










