R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MLD snooping
- Overview
- MLD snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions
- Configuring MLD snooping port functions
- Configuring MLD snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining MLD snooping
- MLD snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD snooping
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- PIM overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Support and other resources
- Index
9
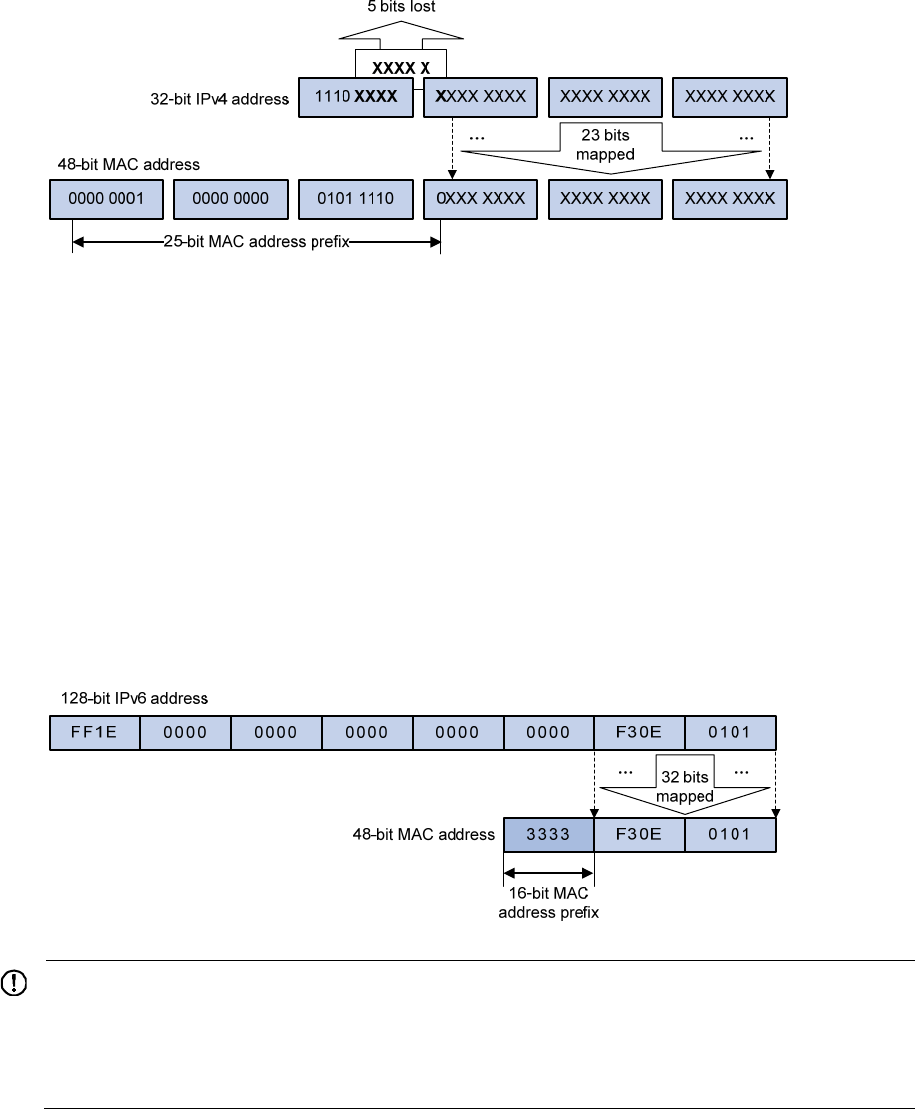
Figure 6 IPv4-to-MAC address mapping
The most significant four bits of a multicast IPv4 address are 1110. Only 23 bits of the remaining
28 bits are mapped to a MAC address, so five bits of the multicast IPv4 address are lost. As a result,
32 multicast IPv4 addresses map to the same IPv4 multicast MAC address. Therefore, a device
might receive some unwanted multicast data at Layer 2 processing, which needs to be filtered by
the upper layer.
• IPv6 multicast MAC addresses:
As defined by IANA, the most significant 16 bits of an IPv6 multicast MAC address are 0x3333
as its address prefix. The least significant 32 bits are the least significant 32 bits of a multicast IPv6
address and are mapped to the remaining IPv6 multicast MAC address, so the problem of
duplicate IPv6-to-MAC address mapping also arises like IPv4-to-MAC address mapping.
Figure 7 An example of IPv6-to-MAC address mapping
IMPORTANT:
Because of the duplicate mapping from multicast IP address to multicast MAC address, the device mi
g
ht
inadvertently send multicast protocol packets as multicast data in Layer 2 forwardin
g
. To avoid this, do no
t
use the IP multicast addresses that are mapped to multicast MAC addresses 0100-5E00-00xx and
3333-0000-00xx (where "x" specifies any hexadecimal number from 0 to F).
Multicast protocols
Multicast protocols include the following categories:
• Layer 3 and Layer 2 multicast protocols:










