R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MLD snooping
- Overview
- MLD snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions
- Configuring MLD snooping port functions
- Configuring MLD snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining MLD snooping
- MLD snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD snooping
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- PIM overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Support and other resources
- Index
10
{ Layer 3 multicast refers to IP multicast working at the network layer.
Layer 3 multicast protocols—IGMP, MLD, PIM, IPv6 PIM, MSDP, MBGP, and IPv6 MBGP.
{ Layer 2 multicast refers to IP multicast working at the data link layer.
Layer 2 multicast protocols—IGMP snooping, MLD snooping, PIM snooping, IPv6 PIM
snooping, multicast VLAN, and IPv6 multicast VLAN.
• IPv4 and IPv6 multicast protocols:
{ For IPv4 networks—IGMP snooping, PIM snooping, multicast VLAN, IGMP, PIM, MSDP, and
MBGP.
{ For IPv6 networks—MLD snooping, IPv6 PIM snooping, IPv6 multicast VLAN, MLD, IPv6 PIM,
and IPv6 MBGP.
This section provides only general descriptions about applications and functions of the Layer 2 and Layer
3 multicast protocols in a network.
The switch supports IGMP snooping, MLD snooping, IGMP, MLD, PIM, and IPv6 PIM. For more
information about these protocols, see the related chapters.
Layer 3 multicast protocols
Layer 3 multicast protocols include multicast group management protocols and multicast routing
protocols.
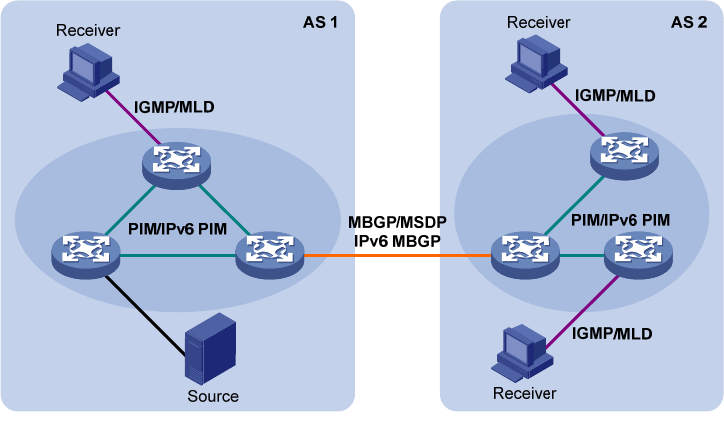
Figure 8 Positions of Layer 3 multicast protocols
• Multicast group management protocols:
Typically, the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) or Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)
protocol is used between hosts and Layer 3 multicast devices that directly connect to the hosts to
define how to establish and maintain their multicast group memberships.
• Multicast routing protocols:










