R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MLD snooping
- Overview
- MLD snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions
- Configuring MLD snooping port functions
- Configuring MLD snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining MLD snooping
- MLD snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD snooping
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- PIM overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Support and other resources
- Index
36
Changing an RPF route
Typically, the topology structure of a multicast network is the same as that of a unicast network, and
multicast traffic follows the same transmission path as unicast traffic does. You can configure a static
multicast route for a given multicast source to change the RPF route, so that the router creates a
transmission path for multicast traffic that is different from the transmission path for unicast traffic.
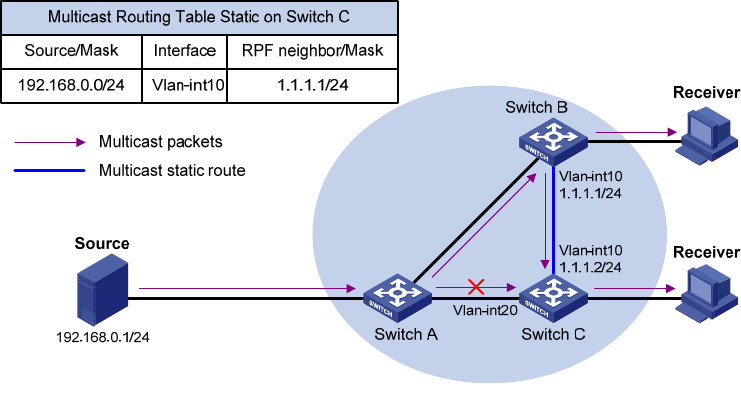
Figure 15 Changing an RPF route
As shown in Figure 15, when no static multicast route is configured, Switch C's RPF neighbor on the path
back to the source is Switch A, and the multicast data from the source travels through Switch A to Switch
C. When a static multicast route is configured on Switch C with Switch B as its RPF neighbor on the path
back to the source, the multicast data from the source travels along the path: Switch A to Switch B and
then to Switch C.
Creating an RPF route
When a unicast route is blocked, multicast forwarding might be stopped due to lack of an RPF route. In
this case, you can create an RPF route by configuring a static multicast route for a given multicast source,
so that a multicast routing entry is created to guide multicast forwarding.










