R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MLD snooping
- Overview
- MLD snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions
- Configuring MLD snooping port functions
- Configuring MLD snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining MLD snooping
- MLD snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD snooping
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- PIM overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Support and other resources
- Index
37
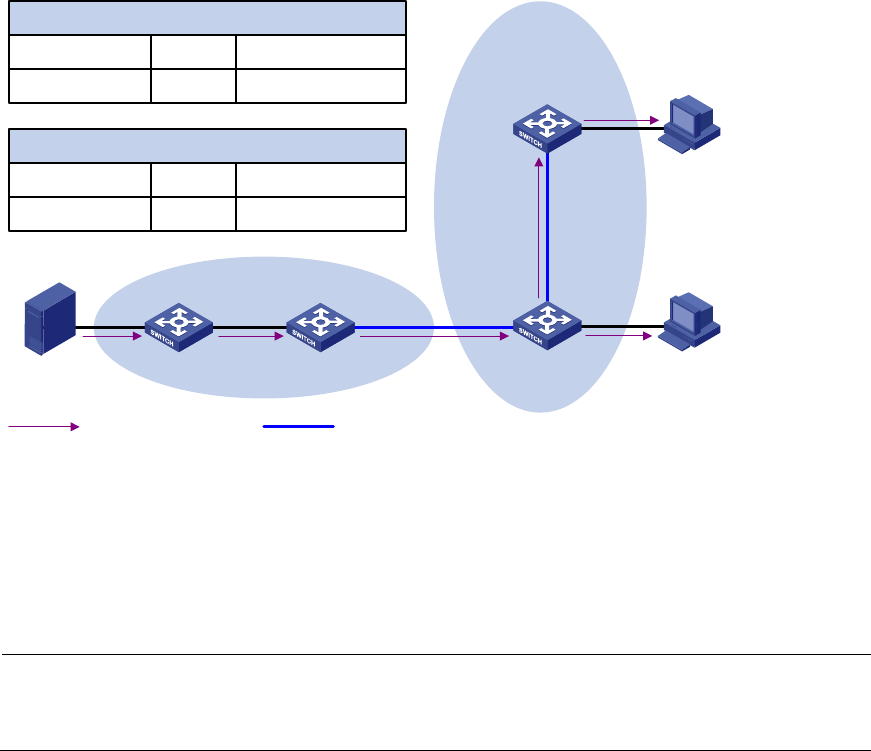
Figure 16 Creating an RPF route
As shown in Figure 16, the RIP domain and the OSPF domain are unicast isolated from each other. When
no static multicast route is configured, the receiver hosts in the OSPF domain cannot receive the multicast
packets from the multicast source in the RIP domain. If you configure a static multicast route on Switch C
and Switch D, specifying Switch B as the RPF neighbor of Switch C and Switch C as the RPF neighbor of
Switch D, the receiver hosts can receive the multicast data from the multicast source.
NOTE:
A
static multicast route is effective only on the multicast router on which it is configured, and will not be
advertised throughout the network or redistributed to other routers.
Multicast forwarding across unicast subnets
Routers forward the multicast data from a multicast source hop by hop along the forwarding tree, but
some routers might not support multicast protocols in a network. When the multicast data is forwarded
to a router that does not support IP multicast, the forwarding path is blocked. In this case, you can enable
multicast forwarding across two unicast subnets by establishing a tunnel between the routers at the edges
of the two unicast subnets.
Vlan-int10
1.1.1.2/24
Vlan-int10
1.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int20
2.2.2.2/24
Vlan-int20
2.2.2.1/24
Source
192.168.0.1/24
Source/Mask
Multicast Routing Table Static on Switch C
192.168.0.0/24
Interface
Vlan-int10
RPF neighbor/Mask
1.1.1.1/24
Source/Mask
Multicast Routing Table Static on Switch D
192.168.0.0/24
Interface
Vlan-int20
RPF neighbor/Mask
2.2.2.2/24
OSPF domain
RIP domain
Switch A Switch B Switch C
Switch D
Receiver
Receiver
Multicast packets Multicast static route










