R21xx-HP FlexFabric 11900 IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MLD snooping
- Overview
- MLD snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions
- Configuring MLD snooping port functions
- Configuring MLD snooping policies
- Displaying and maintaining MLD snooping
- MLD snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD snooping
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- PIM overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Support and other resources
- Index
74
Administrative scoping mechanism
The administrative scoping mechanism effectively releases stress on the management in a single-BSR
domain and enables provision of zone-specific services through private group addresses.
Admin-scoped zones are divided for multicast groups. Zone border routers (ZBRs) form the boundary of
an admin-scoped zone. Each admin-scoped zone maintains one BSR for multicast groups within a
specific range. Multicast protocol packets, such as assert messages and BSMs, for a specific group range
cannot cross the boundary of the admin-scoped zone that provides services for the group range.
Multicast group ranges to which different admin-scoped zones are designated can have intersections.
However, the multicast groups in an admin-scoped zone are valid only within the local zone, and theses
multicast groups are regarded as private group addresses.
The global-scoped zone maintains a BSR for the multicast groups that do not belong to any
admin-scoped zones.
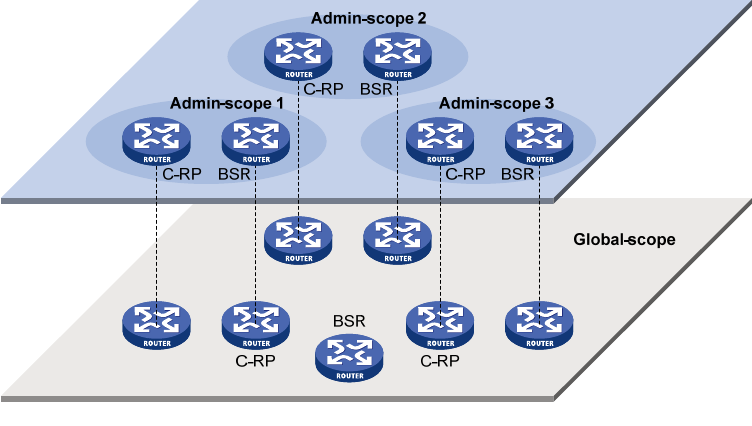
Relationship between admin-scope zones and the global scope zone
The global-scoped zone and each admin-scoped zone have their own C-RPs and BSRs. These devices
are effective only on their respective zones, and the BSR election and the RP election are implemented
independently. Each admin-scoped zone has its own boundary. The multicast information within a zone
cannot cross this boundary in either direction. You can have a better understanding of the global-scoped
zone and admin-scoped zones based on geographical locations and multicast group address ranges.
• In view of geographical locations:
An admin-scope zone is a logical zone for particular multicast groups. The multicast packets for
such multicast groups are confined within the local admin-scope zone and cannot cross the
boundary of the zone.
Figure 30 Relationship in view of geographical locations
As shown in Figure 30, for the multicast groups in a specific group address range, the
admin-scope zones must be geographically separated and isolated. A router cannot belong to










