BLADE OS™ Application Guide HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Version 5.1 Advanced Functionality Software
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Preface
- Part 1: Basic Switching
- Accessing the Switch
- The Management Network
- Local Management Using the Console Port
- The Command Line Interface
- Remote Management Access
- Client IP Address Agents
- Securing Access to the Switch
- Setting Allowable Source IP Address Ranges
- RADIUS Authentication and Authorization
- TACACS+ Authentication
- LDAP Authentication and Authorization
- Secure Shell and Secure Copy
- Configuring SSH/SCP Features on the Switch
- Configuring the SCP Administrator Password
- Using SSH and SCP Client Commands
- SSH and SCP Encryption of Management Messages
- Generating RSA Host and Server Keys for SSH Access
- SSH/SCP Integration with Radius Authentication
- SSH/SCP Integration with TACACS+ Authentication
- End User Access Control
- Ports and Trunking
- Port-Based Network Access Control
- VLANs
- Spanning Tree Protocol
- RSTP and MSTP
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Quality of Service
- Accessing the Switch
- Part 2: IP Routing
- Basic IP Routing
- Routing Information Protocol
- IGMP
- OSPF
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF Implementation in BLADE OS
- OSPF Configuration Examples
- Remote Monitoring
- Part 3: High Availability Fundamentals
- High Availability
- Layer 2 Failover
- Server Link Failure Detection
- VRRP Overview
- Failover Methods
- BLADE OS Extensions to VRRP
- Virtual Router Deployment Considerations
- High Availability Configurations
- High Availability
- Part 4: Appendices
- Index
BLADE OS 5.1 Application Guide
138 Chapter 8: Quality of Service BMD00113, September 2009
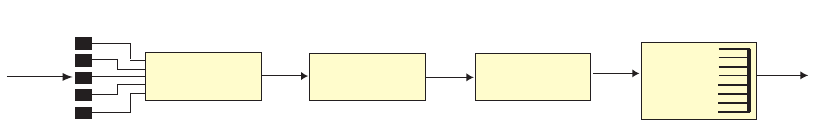
Figure 14 QoS Model
The GbE2c uses the Differentiated Services (DiffServ) architecture to provide QoS functions.
DiffServ is described in IETF RFC 2474 and RFC 2475.
With DiffServ, you can establish policies to direct traffic. A policy is a traffic-controlling
mechanism that monitors the characteristics of the traffic, (for example, its source, destination, and
protocol) and performs a controlling action on the traffic when certain characteristics are matched.
The GbE2c can classify traffic by reading the DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) or IEEE 802.1p priority
value, or by using filters to match specific criteria. When network traffic attributes match those
specified in a traffic pattern, the policy instructs the GbE2c to perform specified actions on each
packet that passes through it. The packets are assigned to different Class of Service (COS) queues
and scheduled for transmission.
The basic GbE2c QoS model works as follows:
Classify traffic:
Read DSCP
Read 802.1p Priority
Match ACL filter parameters
Meter traffic:
Define bandwidth and burst parameters
Select actions to perform on in-profile and out-of-profile traffic
Perform actions:
Drop packets
Pass packets
Mark DSCP or 802.1p Priority
Set COS queue (with or without re-marking)
Queue and schedule traffic:
Place packets in one of two COS queues
Schedule transmission based on the COS queue weight
Ports
ACL
Filter
ACL
Meter
Drop/Pass/
Re-Mark
Classify
Packets
Perform
Actions
Egress
Ingress
COS
Queue
Meter
Traffic
Queue and
Schedule










