BLADE OS™ Application Guide HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Version 5.1 Advanced Functionality Software
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Preface
- Part 1: Basic Switching
- Accessing the Switch
- The Management Network
- Local Management Using the Console Port
- The Command Line Interface
- Remote Management Access
- Client IP Address Agents
- Securing Access to the Switch
- Setting Allowable Source IP Address Ranges
- RADIUS Authentication and Authorization
- TACACS+ Authentication
- LDAP Authentication and Authorization
- Secure Shell and Secure Copy
- Configuring SSH/SCP Features on the Switch
- Configuring the SCP Administrator Password
- Using SSH and SCP Client Commands
- SSH and SCP Encryption of Management Messages
- Generating RSA Host and Server Keys for SSH Access
- SSH/SCP Integration with Radius Authentication
- SSH/SCP Integration with TACACS+ Authentication
- End User Access Control
- Ports and Trunking
- Port-Based Network Access Control
- VLANs
- Spanning Tree Protocol
- RSTP and MSTP
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Quality of Service
- Accessing the Switch
- Part 2: IP Routing
- Basic IP Routing
- Routing Information Protocol
- IGMP
- OSPF
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF Implementation in BLADE OS
- OSPF Configuration Examples
- Remote Monitoring
- Part 3: High Availability Fundamentals
- High Availability
- Layer 2 Failover
- Server Link Failure Detection
- VRRP Overview
- Failover Methods
- BLADE OS Extensions to VRRP
- Virtual Router Deployment Considerations
- High Availability Configurations
- High Availability
- Part 4: Appendices
- Index
BLADE OS 5.1 Application Guide
BMD00113, September 2009 Chapter 2: Ports and Trunking 67
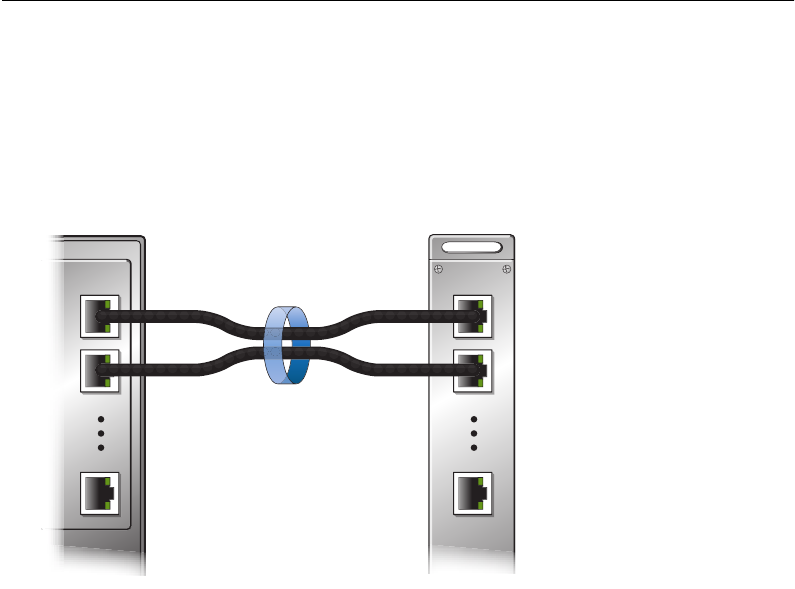
Port Trunk Groups
When using port trunk groups between two switches, as shown in Figure 3, you can create a virtual
link between the switches, operating with combined throughput levels that depends on how many
physical ports are included. Each GbE2c supports up to 12 trunk groups, and each trunk group can
contain up to 8 member ports.
Figure 3 Port Trunk Group
Trunk groups are also useful for connecting a GbE2c to third-party devices that support link
aggregation, such as Cisco routers and switches with EtherChannel technology (not ISL trunking
technology) and Sun's Quad Fast Ethernet Adapter. Trunk Group technology is compatible with
these devices when they are configured manually.
The GbE2c detects broken trunk links (link down or disabled) and redirects traffic to other trunk
members within that trunk group. You can only use trunking if each link has the same configuration
for speed, flow control, and auto-negotiation.
Blade Chassis
Switch
Application
Switch
Aggregate
Port Trunk










