R3102-R3103-HP 6600/HSR6600 Routers IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping querier
- Configuring IGMP snooping proxying
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Configuration prerequisites
- Configuring a multicast group filter
- Configuring multicast source port filtering
- Enabling dropping unknown multicast data
- Enabling IGMP report suppression
- Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join
- Enabling multicast group replacement
- Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages
- Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Appendix
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Overview
- Configuration task list
- Enabling IP multicast routing
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Displaying and maintaining multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuration examples
- Troubleshooting multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Overview
- IGMP configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP functions
- Adjusting IGMP performance
- Configuring IGMP SSM mapping
- Configuring IGMP proxying
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP
- IGMP configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring BIDIR-PIM
- Configuring PIM-SSM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MSDP
- Overview
- MSDP configuration task list
- Configuring basic MSDP functions
- Configuring an MSDP peer connection
- Configuring SA message related parameters
- Displaying and maintaining MSDP
- MSDP configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MSDP
- Configuring MBGP
- MBGP overview
- Protocols and standards
- MBGP configuration task list
- Configuring basic MBGP functions
- Controlling route advertisement and reception
- Configuration prerequisites
- Configuring MBGP route redistribution
- Configuring default route redistribution into MBGP
- Configuring MBGP route summarization
- Advertising a default route to an IPv4 MBGP peer or peer group
- Configuring outbound MBGP route filtering
- Configuring inbound MBGP route filtering
- Configuring MBGP route dampening
- Configuring MBGP route attributes
- Optimizing MBGP networks
- Configuring a large scale MBGP network
- Displaying and maintaining MBGP
- MBGP configuration example
- Configuring multicast VPN
- Overview
- How MD-VPN works
- Multicast VPN configuration task list
- Configuring MD-VPN
- Configuring BGP MDT
- Specifying the source IP address for multicast across VPNs
- Displaying and maintaining multicast VPN
- Multicast VPN configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MD-VPN
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Overview
- Configuration task list
- Enabling IPv6 multicast routing
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 multicast forwarding over GRE tunnel configuration example
- Troubleshooting abnormal termination of IPv6 multicast data
- Configuring MLD
- Overview
- MLD configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD functions
- Adjusting MLD performance
- Configuring MLD SSM mapping
- Configuring MLD proxying
- Displaying and maintaining MLD
- MLD configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- Overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring IPv6 BIDIR-PIM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SSM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP
- Overview
- IPv6 MBGP configuration task list
- Configuring basic IPv6 MBGP functions
- Controlling route distribution and reception
- Configuration prerequisites
- Injecting a local IPv6 MBGP route
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route redistribution
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route summarization
- Advertising a default route to a peer or peer group
- Configuring outbound IPv6 MBGP route filtering
- Configuring inbound IPv6 MBGP route filtering
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route dampening
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route attributes
- Optimizing IPv6 MBGP networks
- Configuring a large scale IPv6 MBGP network
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 MBGP
- IPv6 MBGP configuration example
- Configuring PIM snooping
- Configuring multicast VLANs
- Support and other resources
- Index
281
1. The host sends an MLD done message to all IPv6 multicast routers on the local subnet. The
destination address is FF02::2.
2. After receiving the MLD done message, the querier sends a configurable number of
multicast-address-specific queries to the group that the host is leaving. The destination address field
and group address field of the message are both filled with the address of the IPv6 multicast group
that is being queried.
3. One of the remaining members (if any on the subnet) of the group being queried should send a
report within the time of the maximum response delay set in the query messages.
4. If the querier receives a report for the group within the maximum response delay time, it will
maintain the memberships of the IPv6 multicast group. Otherwise, the querier will assume that no
hosts on the subnet are still interested in IPv6 multicast traffic addressed to that group and will stop
maintaining the memberships of the group.
How MLDv2 works
Compared with MLDv1, MLDv2 provides the following new features.
IPv6 multicast group filtering
MLDv2 has introduced IPv6 multicast source filtering modes (Include and Exclude), so that a host not only
can join a designated IPv6 multicast group, but also can specify to receive or reject multicast data from
designated IPv6 multicast sources. When a host joins an IPv6 multicast group, one of the following
situation occurs:
• If it expects IPv6 multicast data from specific IPv6 multicast sources like S1, S2, …, it sends a report
with Filter-Mode denoted as "Include Sources (S1, S2, …)."
• If it does not expect IPv6 multicast data from specific IPv6 multicast sources like S1, S2, …, it sends
a report with Filter-Mode denoted as "Exclude Sources (S1, S2, …)."
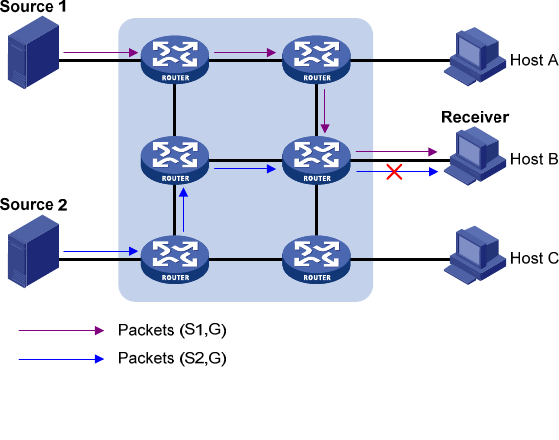
As shown in Figure 80,
the network comprises two IPv6 multicast sources, Source 1 (S1) and Source 2
(S2), both of which can send IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast group G. Host B is interested only in
the IPv6 multicast data that Source 1 sends to G but not in the data from Source 2.
Figure 80 Flow paths of multicast-address-and-source-specific multicast traffic
In MLDv1, Host B cannot select IPv6 multicast sources when it joins IPv6 multicast group G. Therefore,
IPv6 multicast streams from both Source 1 and Source 2 will flow to Host B whether it needs them or not.










