R3102-R3103-HP 6600/HSR6600 Routers IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping querier
- Configuring IGMP snooping proxying
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Configuration prerequisites
- Configuring a multicast group filter
- Configuring multicast source port filtering
- Enabling dropping unknown multicast data
- Enabling IGMP report suppression
- Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join
- Enabling multicast group replacement
- Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages
- Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Appendix
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Overview
- Configuration task list
- Enabling IP multicast routing
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Displaying and maintaining multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuration examples
- Troubleshooting multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Overview
- IGMP configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP functions
- Adjusting IGMP performance
- Configuring IGMP SSM mapping
- Configuring IGMP proxying
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP
- IGMP configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring BIDIR-PIM
- Configuring PIM-SSM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MSDP
- Overview
- MSDP configuration task list
- Configuring basic MSDP functions
- Configuring an MSDP peer connection
- Configuring SA message related parameters
- Displaying and maintaining MSDP
- MSDP configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MSDP
- Configuring MBGP
- MBGP overview
- Protocols and standards
- MBGP configuration task list
- Configuring basic MBGP functions
- Controlling route advertisement and reception
- Configuration prerequisites
- Configuring MBGP route redistribution
- Configuring default route redistribution into MBGP
- Configuring MBGP route summarization
- Advertising a default route to an IPv4 MBGP peer or peer group
- Configuring outbound MBGP route filtering
- Configuring inbound MBGP route filtering
- Configuring MBGP route dampening
- Configuring MBGP route attributes
- Optimizing MBGP networks
- Configuring a large scale MBGP network
- Displaying and maintaining MBGP
- MBGP configuration example
- Configuring multicast VPN
- Overview
- How MD-VPN works
- Multicast VPN configuration task list
- Configuring MD-VPN
- Configuring BGP MDT
- Specifying the source IP address for multicast across VPNs
- Displaying and maintaining multicast VPN
- Multicast VPN configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MD-VPN
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Overview
- Configuration task list
- Enabling IPv6 multicast routing
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 multicast forwarding over GRE tunnel configuration example
- Troubleshooting abnormal termination of IPv6 multicast data
- Configuring MLD
- Overview
- MLD configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD functions
- Adjusting MLD performance
- Configuring MLD SSM mapping
- Configuring MLD proxying
- Displaying and maintaining MLD
- MLD configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- Overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring IPv6 BIDIR-PIM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SSM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP
- Overview
- IPv6 MBGP configuration task list
- Configuring basic IPv6 MBGP functions
- Controlling route distribution and reception
- Configuration prerequisites
- Injecting a local IPv6 MBGP route
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route redistribution
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route summarization
- Advertising a default route to a peer or peer group
- Configuring outbound IPv6 MBGP route filtering
- Configuring inbound IPv6 MBGP route filtering
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route dampening
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route attributes
- Optimizing IPv6 MBGP networks
- Configuring a large scale IPv6 MBGP network
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 MBGP
- IPv6 MBGP configuration example
- Configuring PIM snooping
- Configuring multicast VLANs
- Support and other resources
- Index
312
specified on each router in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain. An RP can serve multiple IPv6 multicast groups, but
a given IPv6 multicast group can have only one RP to serve it at a time.
In most cases, however, an IPv6 PIM-SM network covers a wide area and a huge amount of IPv6
multicast traffic must be forwarded through the RP. To lessen the RP burden and optimize the topological
structure of the RPT, you can configure multiple C-RPs in an IPv6 PIM-SM domain. Among them, an RP is
dynamically elected through the bootstrap mechanism. Each elected RP serves a different multicast group
range. For this purpose, you must configure a BSR.
A BSR serves as the administrative core of the IPv6 PIM-SM domain. An IPv6 PIM-SM domain can have
only one BSR, but can have multiple C-BSRs. If the BSR fails, a new BSR is automatically elected from the
C-BSRs to avoid service interruption. A device can serve as a C-RP and a C-BSR at the same time.
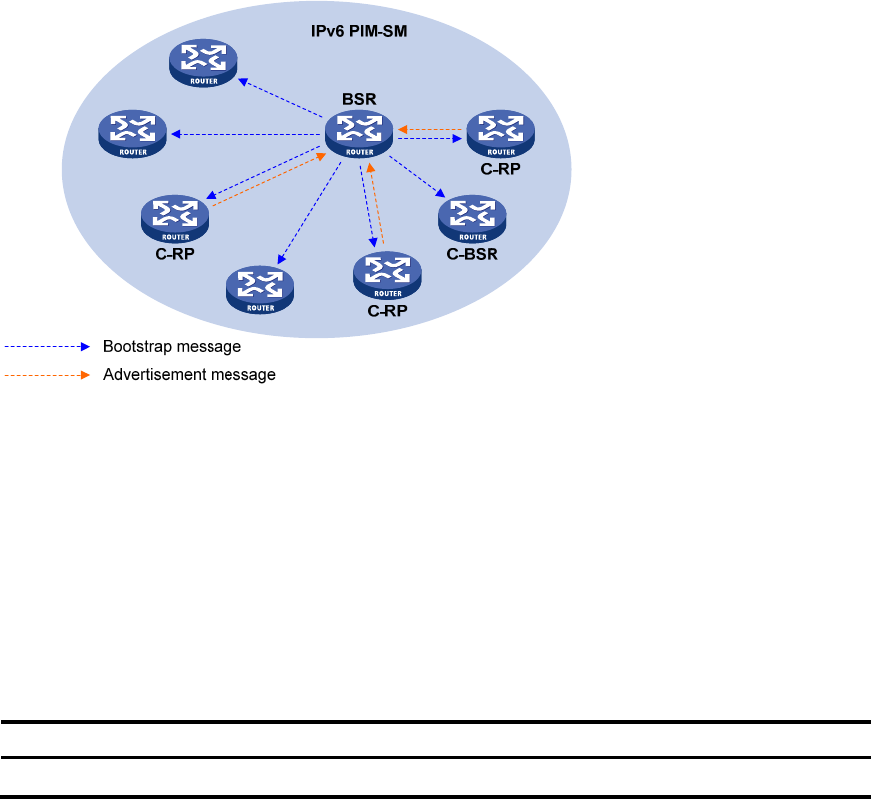
As shown in Figure 91, ea
ch C-RP periodically unicasts its advertisement messages (C-RP-Adv messages)
to the BSR. A C-RP-Adv message contains the address of the advertising C-RP and the IPv6 multicast
group range it serves.
The BSR collects these advertisement messages and chooses the appropriate C-RP information for each
multicast group to form an RP-set, which is a database of mappings between IPv6 multicast groups and
RPs. The BSR then encapsulates the RP-set in the bootstrap messages it periodically originates and floods
the BSMs to the entire IPv6 PIM-SM domain.
Figure 91 BSR and C-RPs
Based on the information in the RP-sets, all routers in the network can calculate the location of the
corresponding RPs based on the following rules:
1. The C-RP with the highest priority wins.
2. If all the C-RPs have the same priority, their hash values are calculated through the hashing
algorithm. The C-RP with the largest hash value wins.
3. If all the C-RPs have the same priority and hash value, the C-RP that has the highest IP address wins.
The hashing algorithm used for RP calculation is "Value (G, M, C
i
) = (1103515245 * ( (1103515245 * (G
& M) + 12345) XOR C
i
) + 12345) mod 2
31
".
Table 12 Values in the hashing algorithm
Value Descri
p
tion
Value Hash value.










