R3102-R3103-HP 6600/HSR6600 Routers IP Multicast Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Multicast overview
- Configuring IGMP snooping
- Overview
- IGMP snooping configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping port functions
- Configuring IGMP snooping querier
- Configuring IGMP snooping proxying
- Configuring IGMP snooping policies
- Configuration prerequisites
- Configuring a multicast group filter
- Configuring multicast source port filtering
- Enabling dropping unknown multicast data
- Enabling IGMP report suppression
- Setting the maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join
- Enabling multicast group replacement
- Setting the 802.1p precedence for IGMP messages
- Enabling the IGMP snooping host tracking function
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP snooping
- IGMP snooping configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP snooping
- Appendix
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Overview
- Configuration task list
- Enabling IP multicast routing
- Configuring multicast routing and forwarding
- Displaying and maintaining multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuration examples
- Troubleshooting multicast routing and forwarding
- Configuring IGMP
- Overview
- IGMP configuration task list
- Configuring basic IGMP functions
- Adjusting IGMP performance
- Configuring IGMP SSM mapping
- Configuring IGMP proxying
- Displaying and maintaining IGMP
- IGMP configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IGMP
- Configuring PIM
- Overview
- Configuring PIM-DM
- Configuring PIM-SM
- Configuring BIDIR-PIM
- Configuring PIM-SSM
- Configuring common PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining PIM
- PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting PIM
- Configuring MSDP
- Overview
- MSDP configuration task list
- Configuring basic MSDP functions
- Configuring an MSDP peer connection
- Configuring SA message related parameters
- Displaying and maintaining MSDP
- MSDP configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MSDP
- Configuring MBGP
- MBGP overview
- Protocols and standards
- MBGP configuration task list
- Configuring basic MBGP functions
- Controlling route advertisement and reception
- Configuration prerequisites
- Configuring MBGP route redistribution
- Configuring default route redistribution into MBGP
- Configuring MBGP route summarization
- Advertising a default route to an IPv4 MBGP peer or peer group
- Configuring outbound MBGP route filtering
- Configuring inbound MBGP route filtering
- Configuring MBGP route dampening
- Configuring MBGP route attributes
- Optimizing MBGP networks
- Configuring a large scale MBGP network
- Displaying and maintaining MBGP
- MBGP configuration example
- Configuring multicast VPN
- Overview
- How MD-VPN works
- Multicast VPN configuration task list
- Configuring MD-VPN
- Configuring BGP MDT
- Specifying the source IP address for multicast across VPNs
- Displaying and maintaining multicast VPN
- Multicast VPN configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MD-VPN
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Overview
- Configuration task list
- Enabling IPv6 multicast routing
- Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 multicast forwarding over GRE tunnel configuration example
- Troubleshooting abnormal termination of IPv6 multicast data
- Configuring MLD
- Overview
- MLD configuration task list
- Configuring basic MLD functions
- Adjusting MLD performance
- Configuring MLD SSM mapping
- Configuring MLD proxying
- Displaying and maintaining MLD
- MLD configuration examples
- Troubleshooting MLD
- Configuring IPv6 PIM
- Overview
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
- Configuring IPv6 BIDIR-PIM
- Configuring IPv6 PIM-SSM
- Configuring common IPv6 PIM features
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PIM
- IPv6 PIM configuration examples
- Troubleshooting IPv6 PIM
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP
- Overview
- IPv6 MBGP configuration task list
- Configuring basic IPv6 MBGP functions
- Controlling route distribution and reception
- Configuration prerequisites
- Injecting a local IPv6 MBGP route
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route redistribution
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route summarization
- Advertising a default route to a peer or peer group
- Configuring outbound IPv6 MBGP route filtering
- Configuring inbound IPv6 MBGP route filtering
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route dampening
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP route attributes
- Optimizing IPv6 MBGP networks
- Configuring a large scale IPv6 MBGP network
- Displaying and maintaining IPv6 MBGP
- IPv6 MBGP configuration example
- Configuring PIM snooping
- Configuring multicast VLANs
- Support and other resources
- Index
47
that received the packet is the RPF interface, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing
interfaces. Otherwise, it discards the packet.
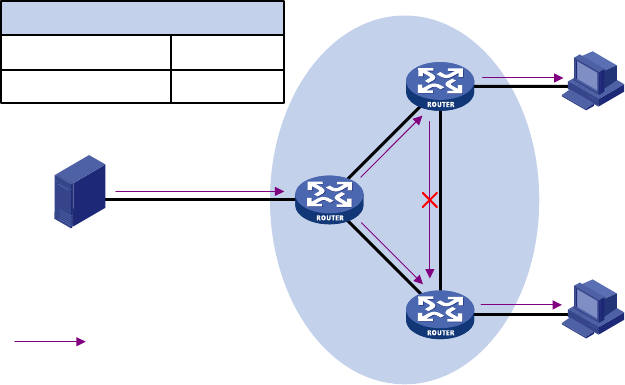
As shown in Figure 18, a
ssume that unicast routes are available in the network, MBGP is not configured,
and no static multicast routes have been configured on Router C. Multicast packets travel along the SPT
from the multicast source to the receivers. The multicast forwarding table on Router C contains the (S, G)
entry, with POS 5/0/1 as the incoming interface.
Figure 18 RPF check process
• When POS 5/0/1 of Router C receives a multicast packet, because the interface is the incoming
interface of the (S, G) entry, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces.
• When POS 5/0/0 of Router C receives a multicast packet, because the interface is not the
incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router performs an RPF check on the packet. The router
searches its unicast routing table and finds that the outgoing interface to Source (the RPF interface)
is POS 5/0/1. It indicates that the (S, G) entry is correct but the packet traveled along a wrong path.
The RPF check fails and the router discards the packet.
Static multicast routes
A static multicast route is an important basis for RPF check. It only affects RPF check but does not guide
multicast forwarding. A static multicast route is also called an "RPF static route".
A static multicast route is effective only on the multicast router on which it is configured, and will not be
advertised throughout the network or redistributed to other routers.
Depending on the application environment, a static multicast route can change an RPF route and create
an RPF route.
Changing an RPF route
Typically, the topology structure of a multicast network is the same as that of a unicast network, and
multicast traffic follows the same transmission path as unicast traffic does. You can configure a static
multicast route for a given multicast source to change the RPF route, so that the router can create a
transmission path for multicast traffic that is different from the transmission path for unicast traffic.
Source
192.168.0.1/24
Receiver
Receiver
Router A
Router B
Router C
POS5/0/1
POS5/0/0
POS5/0/0
Multicast packets
Destination/Mask
IP Routing Table on Router C
192.168.0.0/24
Interface
POS5/0/1