R3303-HP 6600/HSR6600 Routers IP Multicast Configuration Guide
41
[RouterA-vlan100] igmp-snooping querier
# Set the source IP address of IGMP general queries and group-specific queries to 192.168.1.1
in VLAN 100.
[RouterA-vlan100] igmp-snooping general-query source-ip 192.168.1.1
[RouterA-vlan100] igmp-snooping special-query source-ip 192.168.1.1
[RouterA-vlan100] quit
2. Configure Router B:
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] igmp-snooping
[RouterB-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 2/0/4 to the
VLAN.
[RouterB] vlan 100
[RouterB-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 2/0/1 to gigabitethernet 2/0/4
# Enable IGMP snooping and the function of dropping unknown multicast traffic in VLAN 100.
[RouterB-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[RouterB-vlan100] igmp-snooping drop-unknown
[RouterB-vlan100] quit
3. Configure Router C and Router D in the same way as you configure Router B. (Details not shown.)
4. Verify the configuration:
After the IGMP snooping querier starts to work, all the routers but the querier can receive IGMP
general queries. By using the display igmp-snooping statistics command, you can display statistics
for the received IGMP messages. For example:
# Display statistics for the IGMP messages on Router B.
[RouterB] display igmp-snooping statistics
Received IGMP general queries:3.
Received IGMPv1 reports:0.
Received IGMPv2 reports:12.
Received IGMP leaves:0.
Received IGMPv2 specific queries:0.
Sent IGMPv2 specific queries:0.
Received IGMPv3 reports:0.
Received IGMPv3 reports with right and wrong records:0.
Received IGMPv3 specific queries:0.
Received IGMPv3 specific sg queries:0.
Sent IGMPv3 specific queries:0.
Sent IGMPv3 specific sg queries:0.
Received error IGMP messages:0.
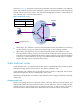
IGMP snooping proxying configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 17, IGMPv2 runs on Router A, and IGMPv2 snooping runs on Router B. Router A
serves as an IGMP querier. Router B is an 6600/HSR6600 router.