R3303-HP HSR6800 Routers IP Multicast Configuration Guide
42
[RouterB-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 2/0/1 to gigabitethernet 2/0/4
# Enable IGMP snooping and the function of dropping unknown multicast traffic in VLAN 100.
[RouterB-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[RouterB-vlan100] igmp-snooping drop-unknown
[RouterB-vlan100] quit
3. Configure Router C and Router D in the same way as you configure Router B. (Details not shown.)
4. Verify the configuration:
After the IGMP snooping querier starts to work, all the routers but the querier can receive IGMP
general queries. By using the display igmp-snooping statistics command, you can display statistics
for the received IGMP messages. For example:
# Display statistics for the IGMP messages on Router B.
[RouterB] display igmp-snooping statistics
Received IGMP general queries:3.
Received IGMPv1 reports:0.
Received IGMPv2 reports:12.
Received IGMP leaves:0.
Received IGMPv2 specific queries:0.
Sent IGMPv2 specific queries:0.
Received IGMPv3 reports:0.
Received IGMPv3 reports with right and wrong records:0.
Received IGMPv3 specific queries:0.
Received IGMPv3 specific sg queries:0.
Sent IGMPv3 specific queries:0.
Sent IGMPv3 specific sg queries:0.
Received error IGMP messages:0.
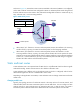
IGMP snooping proxying configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 17, IGMPv2 runs on Router A, and IGMPv2 snooping runs on Router B. Router A
serves as an IGMP querier. Router B is an HSR6800 router.
Configure IGMP snooping proxying on Router B, enabling the router to forward IGMP reports and leave
messages on behalf of attached hosts and to respond to IGMP queries from Router A and forward the
queries to the hosts on behalf of Router A.