R3303-HP HSR6800 Routers MPLS Configuration Guide
207
• PW signaling—The PW signaling protocol is the fundament of VPLS. It is used for creating and
maintaining PWs and automatically discovering VSI peer PEs. Two PW signaling protocols are
available: LDP and BGP.
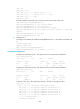
Figure 53 VPLS network diagram
PW establishment
VPLS uses PWs to transfer data over the public network. A PW is established based on an MPLS tunnel
(including LSP and CR-LSP) or a GRE tunnel.
To create a PW, follow these steps:
1. Establish an MPLS tunnel or a GRE tunnel between the local and peer PEs.
2. Identify the address of the peer PE. For PEs in the same VSI, you can manually specify the peer PE
address or you can use a signaling protocol (such as BGP) to automatically discover the peer PE.
3. On each PE, assign a multiplex distinguishing flag (VC label) for the PW and advertise the
assigned VC label to the peer PE to establish a unidirectional VC. The two unidirectional VCs
between the PEs form a bidirectional PW.
According to the PW establishment modes, VPLS is classified into the following types:
• Static VPLS—Uses manually configured VC labels for the PW.
• LDP VPLS—Uses LDP to distribute the VC label for the PW. This mode is also referred to as Martini
mode.
• BGP VPLS—Uses multiprotocol BGP to distribute the VC label for the PW. This mode is also referred
to as Kompella mode.
For more information about the Martini mode and Kompella mode, see "Configuring MPLS L2VPN."
MAC address learning and flooding
VPLS provides reachability by MAC address learning. Each PE maintains a MAC address table.
• Source MAC address learning, which includes the following parts:
{ Remote MAC address learning associated with PWs.
CE 3
VPN 1
Site 2
VPN 2
CE 4
PE 1
PE 2
P
AC
PWSignaling
PW
Site 3
Site 1
VPN 1
VPN 2
CE 1
CE 2
MPLS backbone
Forwarder
Tunnel