Introduction to SNA Capabilities of Tandem NonStop Systems
Connectivity
Introduction to SNA Capabilities of Tandem NonStop Systems–134597
2-8
Supporting Application-to-Application
Communications
Supporting Application-to-Application
Communications
SNAX access methods support several forms of application-to-application
communications:
•
SNA subarea networking between an SNA host and a Tandem NonStop system
running SNAX/XF or SNAX/CDF
•
Session passthrough between applications in SNA distributed processors (such as
the IBM 8100) and applications in an SNA host
•
Advanced peer-to-peer networking (APPN) between a variety of SNA systems (such
as PS/2, AS/400, System/38, System/370 and System/390) and a Tandem NonStop
system running SNAX/APN
APPN is IBM’s strategic direction for SNA and is discussed in more detail below.
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking
Advanced peer-to-peer networking (APPN) is an extension of SNA that enables a
variety of SNA systems (such as PS/2, AS/400, System/38, System/370 and
System/390) to communicate as peers, without the control of a host. The peer systems
must all have the requisite software to function as type 2.1 nodes. There are three types
of type 2.1 nodes, with increasing capabilities:
•
Low-entry networking (LEN) node
•
End node
•
Network node
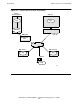
SNAX/APN enables a Tandem NonStop system to participate in this environment as a
LEN node. A LEN node can participate in APPN in two ways:
•
By attaching the LEN node to other type 2.1 nodes (LEN, end, or network nodes)
that are explicitly defined to that LEN node.
•
By attaching the LEN node to a network node, which provides directory and routing
services to the LEN node. Network resources are dynamically registered with a
network node. See Figure 2-5
.
Applications on the Tandem system can communicate with applications on other type
2.1 nodes.
In addition, SNAX/APN supports SNA connections within a Tandem Expand network.