iTP Secure WebServer System Administrators Guide (Version 7.5+)
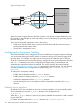
Figure 9 Using a Ticket
Web Client
Internet
iTP Secure WebServer
Subsequent requests are
sent with the same ticket
...so the resource is returned
immediately
URL Request with Ticket
Requested Resource
Again, the ticket is logged. Because the ticket contains a user ID that uniquely identifies the user,
the company in this example can track and analyze a user's Web activity by generating reports
based on the log file.
Two points are especially important to note in this process:
• Tickets work with most Web clients. However, the Web client itself does not know that it is
sending requests that contain tickets.
• The process is transparent to users.
Configuring for Anonymous Ticketing
This section describes how to configure the iTP Secure WebServer to support anonymous ticketing.
You can activate ticketing for specific regions of content to track the use of some file types while
ignoring others. For example, you might want to track accesses of HTML files, but not GIF files.
To set up a content server for anonymous ticketing, configure the server with configuration directives
and Region commands in the server configuration file (httpd.config). Some directives and
commands are required and others are optional. This section discusses the required settings.
“Advanced Configuration Options” (page 174) describes the optional settings. For more general
information about the server configuration file (httpd.config), see “Configuration Directives”
(page 198).
To configure for anonymous ticketing:
• Enable Session Identifiers with the SI_Enable directive.
• Enable anonymous ticketing with the SI_Department directive.
• Initialize the department with the SI_Default directive.
• Activate ticketing for one or more regions with the SI_RequestSI command in the Region
directive.
Enabling Session Identifiers
By default, the iTP Secure WebServer does not use Session Identifiers. You must explicitly enable
Session Identifiers by using the SI_Enable directive in the configuration file:
SI_Enable Yes
When the SI_Enable directive is set to No, any Session Identifier encountered in a URL is treated
as part of the URL.
For further information about the SI_Enable directive, see “SI_Enable” (page 255).
172 Administering Session Identifiers for Anonymous Sessions