Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages Abstract This document consists of this title page, a table of contents, and the Tools Reference Pages for the HP NonStop™ Server for Java™, based on Java 2 Platform Standard Edition 5.0. Product Version HP NonStop Server for Java, based on Java 2 Platform Standard Edition 5.0, Version 5.1 Supported Hardware All HP Integrity NonStop NS-series servers. Supported Release Version Updates (RVUs) This manual supports H06.
529775-001 540386-001 540386-002 544825-001 544825-002 For TNS/R, HP NonStop Server for Java, based on Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition, SDK 1.4.2, Version 2.0 For TNS/E, HP NonStop Server for Java, based on Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition, SDK 1.4.2, Version 1.0 May 2005 HP NonStop Server for Java, based on Java 2 Platform Standard Edition 5.0, Version 5.0 January 2006 HP NonStop Server for Java, based on Java 2 Platform Standard Edition 5.0, Version 5.
Motif, OSF/1, UNIX, X/Open, and the "X" device are registered trademarks, and IT DialTone and The Open Group are trademarks of The Open Group in the U.S. and other countries. Open Software Foundation, OSF, the OSF logo, OSF/1, OSF/Motif, and Motif are trademarks of the Open Software Foundation, Inc. OSF MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THE OSF MATERIAL PROVIDED HEREIN, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
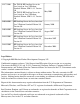
Title Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages Command apt Tool Name Annotation Process Tool dynamic saveabend Dynamic Saveabend File Creation Function Processes program annotations through a set of reflective APIs and a supporting infrastructure. Creates a saveabend file of a running Java program without abending (aborting) the Java program.
jdb Java Debugger Helps you find and fix bugs in Java programs. keytool Key and Certificate Management Tool Manages a database of private keys and their associated certificate chains authenticating the corresponding public keys. kinit Kerberos Tool Obtains and caches Kerberos ticket-granting tickets. klist Kerberos Tool Allows the viewing of entries in the local credentials cache and key table.
Title Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. All rights reserved.
Title Page | Tools Home Page apt: Annotation Processing Tool The apt tool processes program annotations through a set of reflective APIs and a supporting infrastructure. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for apt. Synopsis apt [-classpath classpath] [-sourcepath sourcepath] [-d directory] [-s directory] [-factorypath path] [-factory class] [-print] [-nocompile] [-Akey[=val] ...
Title Page | Tools Home Page dynamic saveabend: Dynamic Saveabend File Creation The Dynamic Saveabend File Creation feature allows you to create the saveabend file of a running Java program, without abending (aborting) the Java program, by issuing a signal to the process. This feature allows the Java program to continue after the abend file is created. The time taken to create the abend file, that is, the application pause time is low (measurable in milliseconds).
Title Page | Tools Home Page extcheck: JAR Conflict Detection Tool The extcheck tool detects version conflicts between a target Java Archive (JAR) file and currently installed extension JAR files. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for extcheck. Synopsis extcheck [ -verbose ] targetfile.jar See Also: jar Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P.
Title Page | Tools Home Page idlj: IDL-to-Java Compiler The idlj tool generates Java bindings from a specified IDL (Interface Definition Language) file. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for idlj. Synopsis idlj [ options ] idl-file Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. All rights reserved.
Title Page | Tools Home Page jar: Java Archive Tool The jar tool combines multiple files into a single Java Archive (JAR) file or retrieves files from a JAR file. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for jar.
Title Page | Tools Home Page jarsigner: JAR Signing and Verification Tool The jarsigner tool generates signatures for Java Archive (JAR) files and verifies the signatures of signed JAR files. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for jarsigner.
Title Page | Tools Home Page java: Java Application Launcher ● Synopsis ● Deviations from Standard Java Options ● -Xeprof ● -Xverbosegc ● Nonstandard Java Options ● Deviations from Nonstandard Java Options ● Deviations from Nonstandard Java -XX Options ● HP Extensions to Standard Java Options ● See Also The java tool launches a Java application by starting a Java run-time environment, loading a specified class, and invoking that class' main method.
-d32 -d64 Selects whether the program is to be run in a 32-bit or 64-bit environment. Note: These options are not valid with NonStop Server for Java 5.1, which uses only the 32-bit environment to run Java programs. -Xeprof The -Xeprof option generates profile data for HPjmeter. The -Xeprof option controls profiling of Java applications running on JRE for NonStop operating system for the Java™ 2 Platform and collects method clock and CPU times, method call count, and call graph.
no -Xeprof option is specified, it is equivalent to: -Xeprof:time_on=sigusr2,time_slice=sigusr2 There is no degradation of performance unless you actually start profiling by the specified signal. times=quick|thorough The quick value instructs the profiler to use the hardware Interval Timer register for time measurement. This value results in faster profiling runs, but in extremely rare circumstances, it can produce bad data. This is the default value.
is attributed to its "caller". The default value for this option is enable. Another way of disabling inlining is to collect the profile data while running the VM in interpreted mode (-Xint), although this is usually much slower. The consequences of inlining for the profiling are: ● The obtained profile data does not reflect faithfully all the calls within the Java code as written by the programmer, but rather as it is actually executed by the VM.
%1 Indicates the type of the garbage collection. 1: represents a Scavenge (GC of New Generation only) %2: indicates if this is a parallel scavenge.
%4: Garbage collection invocation.
exceptions. The default units for n are bytes; n must be greater than 1000 bytes. To modify the meaning of n, append either the letter k (or K) to indicate kilobytes, or the letter m (or M) to indicate megabytes. For example, –Xss10240 and –Xss10k are equal. -Xincgc Specifies using the incremental low-pause garbage collector. This option is supported but using it can lead to about a 10% decrease in garbage collection performance.
for Java 5.1application is run as a Pathway server, you can enable this option to alert Pathmon to restart the server after the NonStop Server for Java 5.1 application dies. -XX:GuaranteeFreeHeapSizeAfterGC= Prevents excessive garbage collection (GC) activity in Java applications that have not been tuned well with respect to GC.
Title Page | Tools Home Page javac: Java Programming Language Compiler The javac tool compiles Java source code into bytecode. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for javac. Synopsis javac [ options ] [ sourcefiles ] [ @argfiles ] Arguments may be in any order. options Command-line options. sourcefiles One or more source files to be compiled (such as MyClass.java). @argfiles One or more files that list options and source files.
Title Page | Tools Home Page javadoc: Java API Documentation Generator The javadoc tool generates API documentation in HTML format from Java source code. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for javadoc. Synopsis javadoc [ options ] { packagenames ] [ sourcefilenames ] [ - subpackages pkg1:pkg2:...
Title Page | Tools Home Page javah: C Header and Stub File Generator The javah tool generates C header files and stub C source files from a Java class. These files provide the connections that allow your Java code and C code to interact. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for javah. Synopsis For files that are needed to implement native methods: javah [ options ] fully-qualified-classname ...
Title Page | Tools Home Page javap: Java Class File Disassembler The javap tool disassembles compiled Java files. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for javap. Synopsis javap [ options ] class ... See Also: ● javac ● rmic ● java ● jdb ● javah ● javadoc Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. All rights reserved.
Title Page | Tools Home Page jdb: Java Debugger The jdb tool helps you find and fix errors in Java programs. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for jdb.
Starting a jdb Session There are many ways to start a jdb session. The most frequent way is to have jdb launch a new Java VM with the main class of application to be debugged. You do this by substituting the command jdb for the command java in the command line.
Basic jdb Commands The following is a list of the basic jdb commands. The Java debugger supports other commands, which you can list by using the jdb help command. {help | ?} Displays the list of recognized commands with a brief description. run After starting jdb and setting any necessary breakpoints, you can use this command to start the execution of the debugged application. This command is available only when jdb launches the debugged application (as opposed to attaching to an existing Java VM).
List the threads that are currently running. For each thread, its name and current status are printed, as well as an index that can be used for other commands, for example: 4. (java.lang.Thread)0x1 main running In this example, the thread index is 4, the thread is an instance of java.lang.Thread, the thread name is main, and it is currently running. thread Select a thread to be the current thread. Many jdb commands are based on the setting of the current thread.
Stepping The step command advances execution to the next line whether it is in the current stack frame or a called method. The next command advances execution to the next line in the current stack frame. Exceptions When an exception occurs for which there is not a catch statement anywhere in the throwing thread's call stack, the Java VM normally prints an exception trace and exits. When running under jdb, however, control returns to jdb at the offending throw.
connector. -launch Launches the debugged application immediately upon startup of jdb. This option removes the need for using the run command. The debugged application is launched and then stopped just before the initial application class is loaded. At that point you can set any necessary breakpoints and use the cont to continue execution. -connect connector-name:name1=value1,... Connects to the target VM through a named connector that uses the listed argument values.
-X option Sets a nonstandard target VM option. Connecting for Remote Debugging i. The Debugger launches the target Java VM. -launch jdb -launch ClassName ii. The Debugger attaches to a previously running Java VM. -attach jdb -attach hostname:portnum For this command, the JVM must already be running as a server at To start the server, use the following command : java -Xnoagent -Xdebug -Djava.
java -Xnoagent -Xdebug -Djava.compiler=NONE \ -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,\ address=hostname:portnum ClassName Transports A Java Platform Debugger Architecture (JPDA) transport is a form of inter-process communication used by a debugger application and the debuggee. NonStop Server for Java 5.1 provides a socket transport that uses the standard TCP/IP sockets to communicate between debugger and the debuggee. NonStop Server for Java 5.1 defaults to socket transport. NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page keytool: Key and Certificate Management Tool The keytool tool manages a keystore (database) of private keys and their associated X.509 certificate chains authenticating the corresponding public keys. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for keytool.
Title Page | Tools Home Page kinit: Kerberos Tool The kinit tool obtains and caches Kerberos ticket-granting tickets. Kerberos is an authentication system to enable two parties to exchange private information across an otherwise open network. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for kinit. Synopsis kinit [ commands ] principal-name Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page klist: Kerberos Display Entries in Credentials Cache and keytab The klist tool allows you to view entries in the local credentials cache and key table. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for klist. Synopsis klist [ commands ] Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. All rights reserved.
Title Page | Tools Home Page ktab: Kerberos Key Table Manager The ktab tool allows you to manage the principal names and service keys stored in a local key table. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for ktab. Synopsis ktab [ commands ] Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. All rights reserved.
Title Page | Tools Home Page native2ascii: Native-to-ASCII Converter The native2ascii tool converts a file that has native-encoded characters (characters that are not Latin-1 and not Unicode) to a file with Unicode-encoded characters. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for native2ascii. Synopsis native2ascii [ options ] [ inputfile [ outputfile ] ] Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page nsjps: NonStop Java Virtual Machine Process Status Tool The NSJPS tool is a process status tool that lists and monitors the Java processes running on a system. Synopsis nsjps [ ] The following options are supported: Option Purpose -cpu Lists the Java processes running on the CPU. -user Lists the Java processes owned by a user.
-help Prints the nsjps help text. -count Repeats the listing for the specified number of times. -delay
Title Page | Tools Home Page orbd: Object Request Broker Daemon The Server Manager included with the ordb tool enables clients to transparently locate and invoke persistent objects on servers in the CORBA environment. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for orbd. Synopsis orbd -ORBInitialPort nameserverport [ options ] See Also: ● Naming Service ● servertool Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page rmiregistry: Java Remote Object Registry The rmiregistry tool starts a remote object registry on the specified port on the current host. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for rmiregistry. Synopsis rmiregistry [ port ] See Also: ● java ● java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry ● java.rmi.Naming Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page rmic: Java RMI Compiler The rmic tool generates stubs and skeletons for remote objects that use either the JRMP or Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP). The rmic tool also generates Object Management Group (OMG) Interface Definition Language (IDL). For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for rmic. Synopsis rmic [ options ] package-qualified-classname ...
Title Page | Tools Home Page rmid: Java RMI Activation System Daemon The rmid tool starts the activation system daemon that allows objects to be registered and activated in a Java virtual machine (VM). For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for rmid. Synopsis rmid [ options ] See Also: ● java ● CLASSPATH in the NonStop Server for Java Programmer's Reference rmic ● Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page serialver: Serial Version Command The serialver tool returns the serialVersionUID of one or more classes. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for serialver. Synopsis serialver [ option ] [ classname ... ] See Also: ● java.io.ObjectStreamClass Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference Pages (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P. All rights reserved.
Title Page | Tools Home Page servertool: Java IDL Server Tool The servertool tool provides a command-line interface for application programmers to register, unregister, start up, and shut down a persistent server. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for servertool. Synopsis servertool -ORBInitialPort nameserverport options [ commands ] See Also: ● orbd Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.
Title Page | Tools Home Page tnameserv: Naming Service Access The tnameserv tool starts the Java Interface Definition Language (IDL) name server to provide access to the CORBA Common Object Services (COS) Naming Service. For a complete description of the tool and its use, see the Sun Microsystems documentation for Naming Service. Synopsis tnameserv [ -ORBInitialPort n ] Title Page | Tools Home Page NonStop Server for Java 5.1 Tools Reference (544825-002) © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company L.P.